24-Port Gigabit Switch Selection
An Ethernet switch acts as a bridge to connect different parts of a network together. Although many routers also possess the network switching capabilities and multiple Ethernet ports, the Ethernet switch is not the replacement for routers. It is worth emphasizing that Ethernet switches are smarter than routers in that they operate at the data link layer (Layer 2) and the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI Reference Model and therefore support any packet protocol. Ideally, switches will make better use of bandwidth if you prefer wired to wireless connections but have more devices than available Ethernet ports. On the other hand, an Ethernet switch is a costly way to expend the network in home or small business. So it is very important to invest an Ethernet switch with the appropriate number of ports to fit your needs. In the midst of various Gigabit Ethernet switches, a 24-port switch is considered as the most common Gigabit switch that connect devices in a local area network. Then this article will explore how to select a suitable 24-port Gigabit switch.
FS S3800-24F4S 24-port Gigabit switch comes with 20x 100/1000BASE SFP, 4x 1GE combo and 4x 10GE SFP+ slots. The flexible port combination form provide a high bandwidth aggregation connectivity for multiple switch in network to enhance network capacity. Moreover, it is a stackable SFP managed switch, which can provide true stacking of up to 4 switches in a stack acting as a single unit with totally 106 ports (96x 1G Ports and 10x 10G ports). The switching capacity is 128Gbps. This 24-port Gigabit managed switch fits for enterprise network operators who need high performance and low power processor to provide full speed forwarding and line-dormant capacity.

Figure 1: FS S3800-24F4S 24-Port Gigabit Switch
Cisco SGE2000P comes with 24 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 ports and 4 shared Gigabit SFP slots. This 24-port Gigabit managed switch can provide ACL (access control lists), DoS (denial-of-service), VLAN and IEEE 802.1X port authentication. And the enhanced quality of service (QoS) and traffic-management features help ensure clear and reliable voice and video communications. This Gigabit network switch enable you to take advantage of the comprehensive feature set for a better-optimized, more secure network.

Figure 2: Cisco SGE2000 24-Port Gigabit Switch (Source: Cisco)
The Netgear ProSafe GS724T is armed with 24 copper 10/100/1000 ports and 2 SFP 100/1000 ports. Each port can transfer data at maximum throughput for a total maximum switching speed of up to 48 Gbps. This 24-port switch is intended for SMB organizations using the switch for applications like VoIP, video conferencing, and system security, etc. And it features a fanless system, allowing the switch to work silently without overheating. This is great for use on homelab, as its quiet operation won’t cause a distraction.

Figure 3: NETGEAR ProSAFE GS724T 24-Port Gigabit Switch (Source: NETGEAR)
The TP-Link TL-SG1024 features 24 Gigabit Ethernet ports and non-blocking switching, which can provide large file transferring and also be compatible with 10Mbps and 100Mbps Ethernet devices. Moreover, this network switch has 48Gbps switching capacity with 8K MAC address table, 10KB Jumbo Frame and 4MB buffer memory. This TP-Link switch is a fanless rack mount design with LED diagnostic lights, so you can easily tell which ports are in use. It can automatically adjust power consumption according to the link status to limit the carbon footprint of your network. The price is $69.99 on Amazon. So this fanless Ethernet switch is good for your wallet both because it is inexpensive to buy and because of its energy-saving technology.

Figure 4: TP-Link TL-SG1024 24-Port Gigabit Switch(Source: TP-Link)
| Gigabit Switch Mode | Ethernet ports | Gigabit SFP | SFP+ Uplink ports | Switching Capacity | Forwarding Rate | Power Consumption | Price |
| FS S3800-24F4S | 24 | 4 combo | 4 | 128Gbps | 95Mpps | ≤60W(Full-loaded) | $449 |
| Cisco SGE2000 | 24 | 4 | / | 48Gbps | 35.7Mpps | 90W | $390 |
| NETGEAR ProSAFE GS724T | 24 | 2 | / | 48Gbps | No Information | 29W | $219.99 |
| TP-Link TL-SG1024 | 24 | / | / | 48Gbps | 35.7Mpps | 13.1W | $69.99 |
From the chart we can see, all the Gigabit switches listed above provide 24 port Ethernet RJ45 ports, only FS S3800-24F4S 24-port Gigabit switch has 4 SFP+ uplink ports. They have some characteristics in common that make them suitable for being used in places like home or small business office. In terms of the power consumption, TP-Link TL-SG1024 and NETGEAR ProSafe GS724T are lower than others, but the huge price spread exists between these two switches because NETGEAR ProSafe GS724T has another two SFP ports for more flexible application. Among these four switches, if you have no limited cost budget, FS S3800-24F4S is a good choice. It has more flexible port combination and higher switching capacity, that is why it may cost a little more than the other three switches. If you need stronger data transferring capability, FS S3800-24F4S is a better choice considering its forwarding rate. On the contrary, TP-Link TL-SG1024 is the best budget choice. If you want a fanless switch, NETGEAR ProSafe GS724T is an inexpensive and reliable choice, but the install program only works on Windows and the secure management is very difficult to be enabled.
When choosing a Gigabit Ethernet switch, the first factor to consider is how many devices need to be networked together. Purchasing a network switch with too few ports and not enough capacity will prove ineffective, and one that is too large can be a waste of money. Generally, small offices with a few employees should start with a 16-port switch, but a business that is looking to expand its operations soon needs a 24-port switch. So 24-port Gigabit switch is the most future-proofing and cost-effective choice in small business network.
Related Article: 48-Port 10GE Switch Selection: What Is the Right Choice?
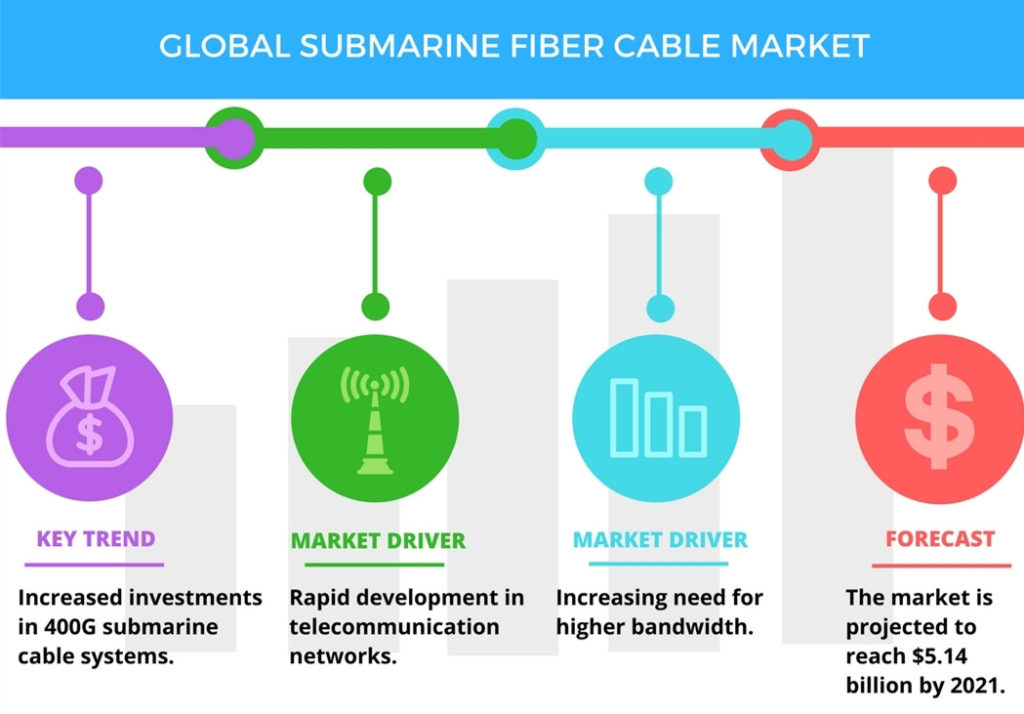
Good Forecasts for Global Optical Fiber Cable Market
An optical fiber cable uses light wave for voice and data transmission, its data transmission capacity is 4.5 times more than conventional copper cables. So in the past several decades, we have seen that fiber optic cables are superior to traditional copper twisted-pair cable or coaxial cable because of its unique physical characteristics, allowing information to travel at speeds increasingly approaching the speed of light without interference between adjacent wavelengths. In leading market, the global drive to implement FTTx into more new venues is good news for the market of optical fiber cables. Another good trend is that the price erosion of optical fiber cables had been 10 to 15 percent annually, in result that the demand of optical fiber cable is expected to continue growing in the foreseeable future. And the growing data transmission workloads placed by high-performance computers, servers and network storage systems is helping spur growth in the market. Consequently, fiber optic cables are now the indispensable backbone of today’s communication network. This article will analyse the global optical fiber cable market in three main applications, including long-distance communication, submarine cable and FTTx network.

According to the report "Fiber Optics Market by Cable - Global Forecast to 2021”, the optical fiber cable market is anticipate to grow at a CAGR of over 9.8% during 2016-2021. The growing importance of cloud computing, data transfer & storage, and IoT is driving the use of Internet, which is driving the fiber optic cable market, as it acts as the backbone for data transmission. Moreover, growing technological advancements increase in number of connected devices and data centers are expected to positively influence global optical fiber cable market. In addition, next generation technologies such as LTE and FTTx, which require last mile connectivity, is expected to propel the demand for optical fiber cables in the coming years. All these factors have led to an increase in Internet users, which in turn has led to the higher usage of optical fiber cable to transfer information over the Internet, thus driving the fiber optics market.
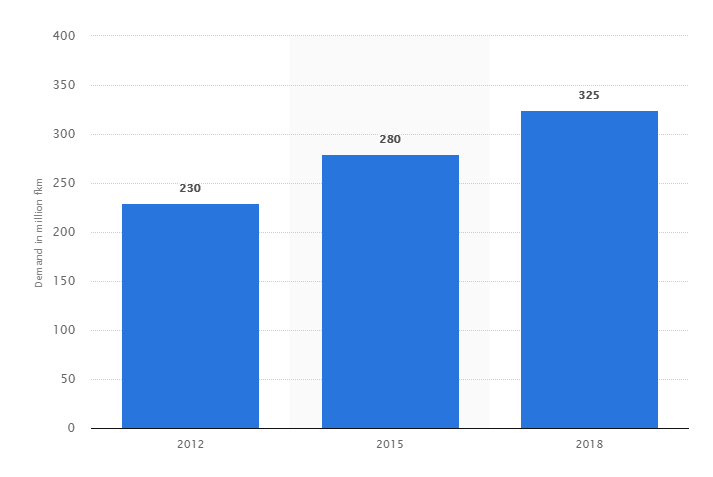
Global Optical Fiber Cable Demand from 2012 to 2018 (Source: Statista)
Currently, the growing adoption of optical technology in the telecommunications appears to be promising. Optical fiber has virtually unlimited capacity and low signal attenuation allowing long distances without amplifier or repeater, no exposure to parasite signals or crosstalk, and no electromagnetic interference (EMI). So fiber optic cable is especially advantageous for high-speed data transfer services in long-distance communications over electrical cabling. Furthermore, the increasing cloud-based applications, audio-video services, and Video-on-Demand (VoD) services further stimulate the demand for optical fiber cable installations.
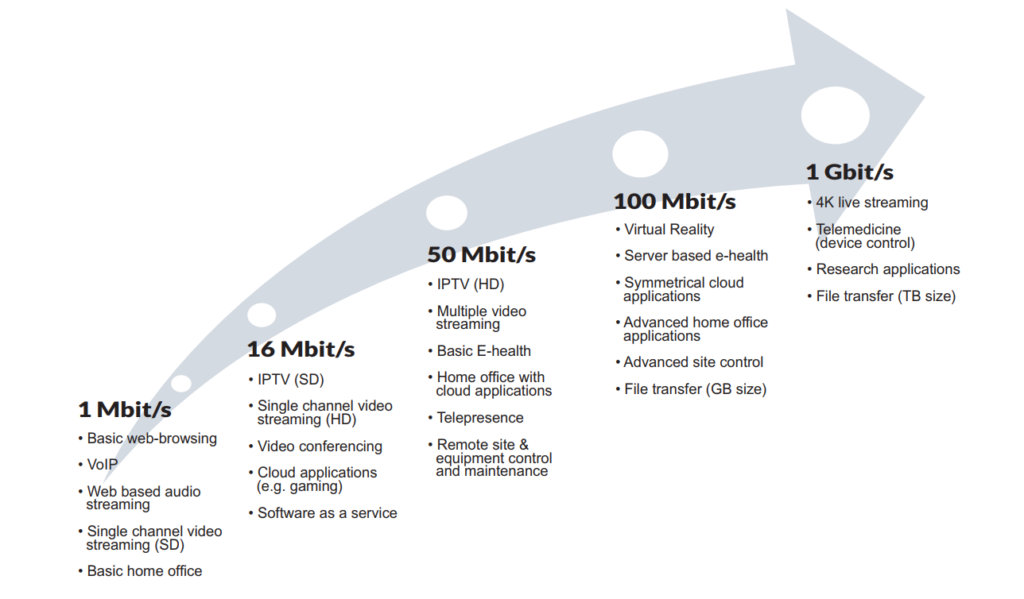
Growing Need for Capacity (Source: Goldmedia)
Submarine optical fiber cables are undersea cables used for carrying data across interconnected networks between continents. With the advancements of technology, most of the submarine optical fiber cables that currently form the backbone of the Internet connect the U.S. to Europe and Asia by crossing the Atlantic or Pacific oceans. Instead, there is a proposal for deployment of Trans-polar submarine cable system in Arctic Ocean. Laying an undersea fiber optic cable is meant to connect Asia and Europe by crossing the Arctic Circle - the shortest practical distance yet for Internet signals traveling between the two continents. According to the report by Global Industry Analysts (GIA), cumulative installations of submarine optical fiber cables globally are projected to reach 2 million kilometers by 2020, driven by the growing demand for fiber broadband and the ensuing deployment of fiber optic cables in the Internet backbone. Presently, submarine optical fiber cables transmit 100% of the international Internet traffic, and more than 95% of the world’s combined data and voice traffic.
Submarine Optical Fiber Cable Market (Source: Technavio)
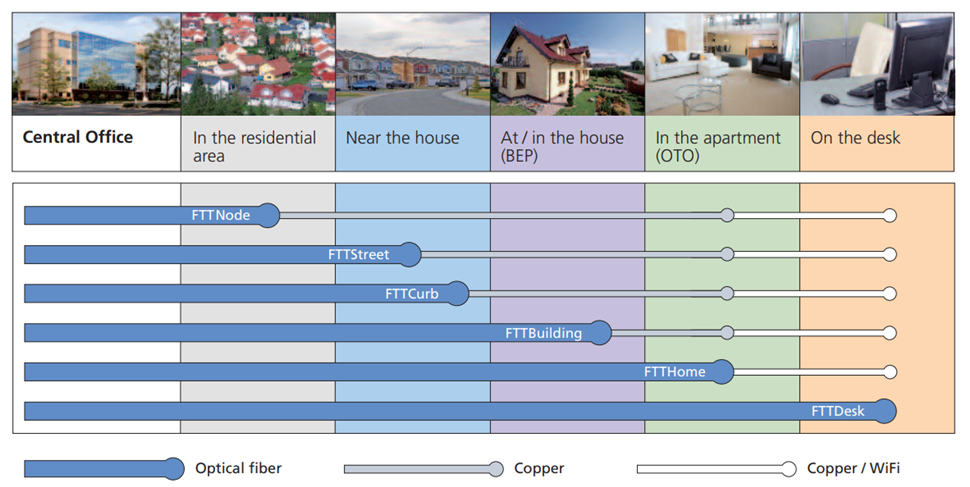
In recent years, the market for optical fiber cable has shifted dramatically to local deployments, away from long haul and regional. This is the impact of FTTx, which calls for far more dense applications in neighborhoods, cities and other highly focused areas. Optical fiber cable is being caught up in the global move to broadband in the near future. The next generation of high bandwidth applications, along with the proliferation of connected devices, is expected to require faster and higher bandwidth networks which will require the use of multimode fiber cable for data transfer. This growth in the FTTx networks in turn is expected to drive the fiber optics market. Future Market Insights (FMI) forecasts the global fiber to the home (FTTH) market's value will grow from $9.5 billion in 2017 to more than $37 billion by the end of 2027, a 14.4% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). In the leading Asian economies, more than 44% of all homes and buildings are already directly connected to the fiber optic cable network; in North America penetration is 8.4%, in Europe 5.6%.
Fiber optic cable is widely used for data transmission and is increasingly being used in place of metal wires because of its efficiency and high transmission capacity. Since the use and demand for great bandwidth and fast speed, there is no doubt that fiber optic transmission will bring more opportunities and be continuously researched and expanded to cater for future demands. However, although fiber optic cable in itself is considered a long-term stable investment, it also faces huge challenge. The major restraint in the fiber optics market is the growing use of wireless communications systems in remote areas.
Related Article: The Advantages and Disadvantages of Fiber Optic Transmission
Power over Ethernet Switch: Passive PoE Vs Active PoE
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology for wired LANs. This allows a single cable usually Ethernet cable to provide both data connection and electric power to devices such as IP cameras, NVR recorders, wireless access points, etc. A PoE switch, compared with other Gigabit network switches, has power over Ethernet injection built in. This feature allows end-user to power PoE capable devices without the need for a separate power supply or the need for an electrical outlet near the powered device. If you have read about the how-to-understand-poe-and-poe-switches, you must know clearer about the difference between PoE and PoE+ switches. However, today’s article will help you understand active PoE and passive PoE.
As mentioned before, a PoE switch not only supply power to devices but also carries network connection. In general, a PoE switch usually contains multiple Ethernet ports, e.g. a PoE switch with 8 ports, PoE switch with 16 ports, 24 ports PoE switch, or PoE switch with 48 ports. If you are looking for PoE switch to cover all your devices, it’s important to check the port number first.
To safeguard a voltage range, the Power over Ethernet devices must communicate according to established procedures. In simple terms, active PoE refers to any type of PoE that negotiates the correct voltage between the switch and PoE-powered device. Passive PoE does no such negotiation, and as such is always sending electric current out over the Ethernet cable at a certain voltage regardless of the device it’s going to.
If your PoE switch uses 48V 802.3af or 802.3at standard, it is considered to be active PoE. The power supply unit inside the active PoE switch usually tests the connection before providing the supplying voltage, meaning that PoE switch will check the power coming in, and if it doesn’t meet the device requirement, it won’t power up.
Passive PoE refers to any devices using PoE that is not 802.3af or 802.3at. Unlike active PoE switch, In passive PoE, no negotiation takes place between the two devices, but instead the known cable layout is used from Standard 802.3af, mode B. Therefore, it is extremely important to know what PoE voltage your devices requires before plugging in the Ethernet cable and powering it up. If you connect the wrong voltage, you may cause permanent electrical damage. Passive PoE is like plugging a 120V appliance into a 240V outlet, but with devices than cost much more than a simple toaster.
The big advantage of Power over Ethernet switch is that it allows greater flexibility in locating devices, as you don't have to be situated near a power source—power is carried to them right in the Ethernet cable. That also frequently results in significantly lower installation costs, especially where many Access Points must be setup. The difference between Passive PoE and active PoE switch is quite obvious. For more, you can go through previous articles.
10GBASE-T SFP+ Copper Module up to 200m – Is It Possible?
The introduction of 10gb SFP+ copper modules made people rethink 10G optical network, and was treated as the thrive of copper cabling. Vendors like Cisco, HPE, Amazon, prolabs and FS.COM provides 10GBase-T SFP+ module around $300 with 30m linking length and 2.5W power consumption, but it is a controversial and expensive copper devices. Today’s article decodes the 10GBASE-T SFP+ copper modules that can support up to 200m, and auto-negotiate to 1G, 2.5G, 5G data rate.

10GBASE-T Copper Can Auto-negotiate to 5G, 2.5G, 1G, 100Mbps, 10Mbps
10GBASE-T SFP+ transceivers, terminated with RJ45 connectors, allow 10G bandwidth over existing infrastructure and reuse Ethernet cables. However, owing to the high price and unstable performance, 10GBASE-T is not usually the type when competing with cost-effective DAC cables, and reliable SFP+ fiber modules. Customers use ideally DAC twinax cables for shorter reach transmission, or if they need longer distance, they would go for fiber SFP+ or SFP+ AOC cables.
10GBASE-T can auto-negotiate to 5G, 2.5G, 1G, 100Mbps, 10Mbps data rate, which is the highlight of this product. For 2.5GBASE-T/5GBASE-T networks, you can use this module.
Is It Possible to Support up to 200m?
The regular 10G copper modules launched by fiber optic vendors are specified to support up to 30m over Cat6a/Cat7 cables. According to wikipedia, 10GBASE-T, or IEEE 802.3an-2006 standard is released to provide 10G connections over unshielded or shielded twisted pair cables, with distances up to 100 meters (Cat6a), 55m (Cat6). What’s more, 10GBASE-T cable infrastructure can also be used for 1000BASE-T allowing a gradual upgrade from 1000BASE-T using auto-negotiation to select which speed to use.
Therefore, 10GBASE-T copper modules can auto-negotiate to lower data rate e.g. 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 2.5 Gbps, 5 Gbps, 10 Gbps. A new type 10GBASE-T SFP+ from Mikrotik can support all the above five data rates over different link length. The max power consumption is 2.4W, and can only be used in SFP+ ports.
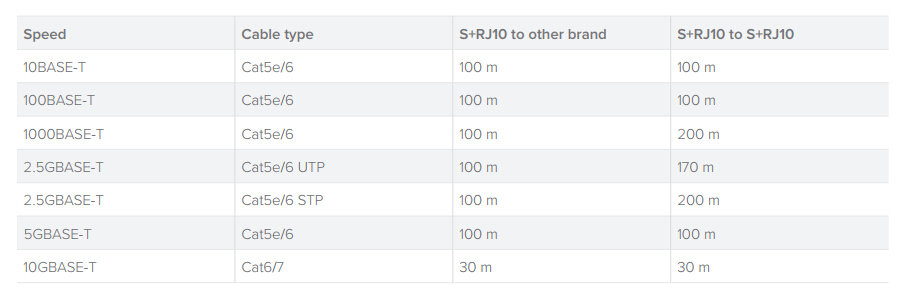
Table 2 shows the 10GBASE-T Cable Types and max supported lengths.
According to the above table, we can see that it can reach up to 200m over 1000BASE-T network, or at 2.5G 200m using Cat6a STP cables. So please be mindful of where you want to use them.
Isn’t 10GbE Copper Power Hungry?
10GBASE-Cu DAC twinax cables consumes 4-8 Watts power during the operation, while SFP+ 10GBASE-T copper modules draw less (2.5W), and it is not a standard compliant transceiver, hence the shorter distance of 30m. But if dig deeper, we will find that if there were more power, they would use it. So, in order to be fully compatible with 10GBASE-T standard, you need more power.
Today's fiber SFP+ modules like 10GBASE-SR draw less than 1W, much lower than the 5 to 8 Watts per 10GBASE-T port. Drawing an increase in power by a factor of 5 can seem like an expensive upgrade cost. When factored against servers that can draw up to 1000W or more, the overall proportion is low. For small to mid-sized (SMB) organization switch-server installations, short reach cable runs of less than 45 meters will apply and use even less power and therefore cost less.
Future-Proof 10GBase-T Technology
Although fiber becomes popular with the benefit of delivering flexible cabling, lowest latency, many IT departments still adopt copper cables for switch-to-switch or switch-to-server connections in 10G Ethernet applications. 10GBase-T Copper SFP+ is backward compatible with Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet and can automatically negotiate to lower speed connections. More importantly, 10GBase-T provides a cost-effective method for migrating from your current network to 10G Ethernet by utilizing your existing RJ-45 copper short connections. Amazon, FS.COM, Prolabs, Mikrotik and HPE supply 10GBAST-T copper transceivers, you can get what you want from them.
Reach to 40km Transmission – 100G QSFP28 ER4 Lite Module
Today’s world is undergoing an infrastructure transformation, which requires higher speed, greater scalability, higher performance, flexibility and reliability to meet the demands. Take 100G data rate as an example, the MSA groups keep driving development of 500m, 2km, 10km and 40km cost-effective 100G optics targeting modern data center. The 100G QSFP28 ER4-Lite standard was sampling several months ago, but now we are glad to announce that 100G QSFP28 ER4 modules are available in several vendors, e.g. FS.COM, Flexoptics, Smartoptics, etc. Today’s article will explain this long-reach 100G optics in detail.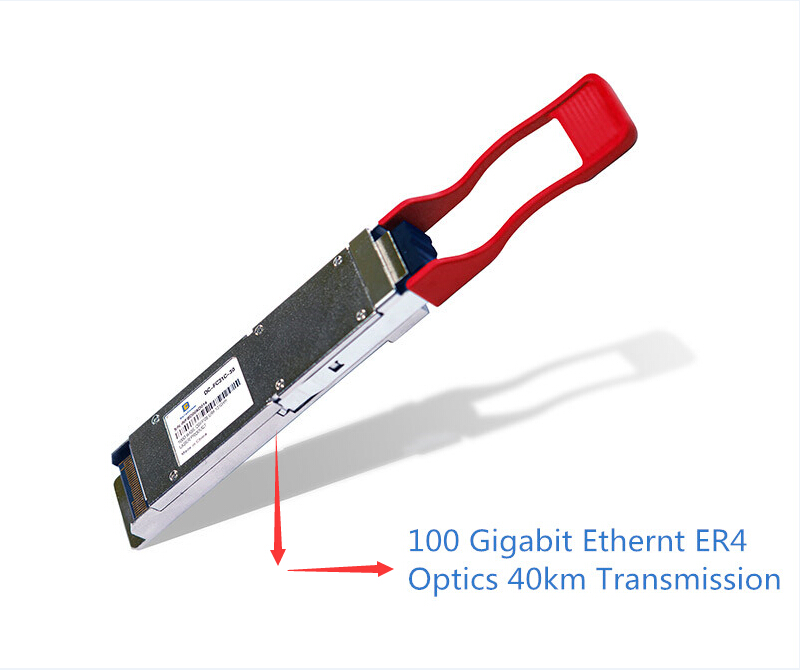
How Does It Develop?
A heated topic—how to reach beyond 10km in 100G network aroused much attention in Reddit. For applications beyond 10km, 100GBASE-ER4 is proposed. This type of optical transceivers are manufactured by using a semiconductor amplifier (SOA) inside the transceiver to increase power budget. However, 100G ER4 is available in CFP and CFP2 form factors, but because of the large form factor and power consumption, they are seldom utilized in 100G long-reach applications. What’s worst, the newly launched 100G optical switches are commonly equipped with compact QSFP28 ports instead of larger CFP interface.
These extended reaches are preferring to use high-density 100G QSFP28 modules to maximum capacity and minimize space, power usage and maintenance cost. The CWDM4 MSA defined the first duplex low-cost 100G specification for 2km reaches based on a CWDM grid and using RS (528,514) FEC. Now the 4WDM MSA is extending the value proposition of the CWDM4 MSA and RS-FEC to define an even more cost-effective set of specifications for reaches from 10 to 40 km. Customers, particularly hyperscale cloud service providers and carriers, are looking for optimized solutions for up to 40 km.
What’s New with QSFP28 ER4-Lite Solution?
QSFP-100G-ER4L-S is designed for extended reach 100 Gigabit Ethernet link. The 100GBASE-ER4-Lite QSFP28 supports both 100GbE and OTU4 applications over single-mode fibers, and supports up to 40km with FEC and up to 30km without FEC. 100G QSFP28 ER4 Lite module consumes 4.5W power in max.

The 100 Gigabit Ethernet signal is carried over four independent channels over four LAN-WDM wavelengths—1296nm, 1300nm, 1305nm, 1309nm. Multiplexing and demultiplexing of the four wavelengths are managed within the device. This QSFP28 was standardized by ITU-T as G.959.1 4L1-9D1F and 4-Wavelength WDM MSA Group. The following table displays the existing 100G QSFP28 MSA optics in detail.
| Product | Description | Connector Type |
| QSFP-100G-SR4-S | 100GBASE SR4 QSFP Transceiver, 100m over OM4 MMF | MPO-12 (12 fibers) |
| QSFP-100G-LR4-S | 100GBASE LR4 QSFP Transceiver, 0km over SMF | LC |
| QSFP-100G-CWDM4-S | 100GBASE CWDM4 QSFP Transceiver, 2km over SMF | LC |
| QSFP-100G-PSM4-S | 100GBASE PSM4 QSFP Transceiver, 500m over SMF | MPO-12 (12 fibers) |
| QSFP-100G-ER4L-S | 100GBASE ER4 Lite QSFP Transceiver, 25-40km over SMF | LC |
The 100G QSFP ER4-Lite module will interoperate with existing ER4 solutions in the field up to 30km. Foe example, QSFP100 ER4-Lite provides backward compatibility with Cisco’s CPAK ER4-Lite, whose reach is up to 25km, and with IEEE 100GBASE-ER4 standardized transceivers, such as CFP 100G ER4, up to 30km. It also interoperates with QSFP28 and CPAK IEEE 100GBASE-LR4 modules up to 10km.
40km Transmission With FEC Turn On
To reach 40km transmission, QSFP ER4 lite requires the use of FEC on the host platform. So what is FEC? Forward Error Correction (FEC) can turn a mediocre to bad BER into a good BER. Ethernet network usually uses FEC in 1000BASE-PX (EPON), 10GBASE-KR, 10GEPON, 10GBASE-T, DSL, etc. High end long haul telecom industry also requires FEC. P802.3ba links have limited power budgets and SNR, for e.g. eye safety reasons.
Conclusion
The migration of current network infrastructure to 100G systems is inevitable, and a growing number of enterprises require 100G client interface to extend up to 40km without the use of expensive optical amplifiers. Thus, the new ER4-Lite specification enables cost-effective 100G 40km pluggable solutions in compact QSFP28 transceivers that use Forward Error Correction (FEC) and APD-based receivers. Such evolution is very exciting for not only everyone involved in its development and construction, but also for all those who seek a simple, reliable and cost-effective solution to extend the reach of their networks, without expensive network upgrades. FS.COM is devoting to change the world with our cost-effective self-developed devices, if you are interested, please feel free to contact us.
Power Supply: POE Switch for IP Camera
PoE switch, as the previous article describes, provides power and data to all PoE devices, including IP cameras, NVR recorders, computers, and VoIP phones, etc, via a single Ethernet cable (Cat5, Cat5e or Cat6). A PoE switch normally comes with multiply ports to support more than one IP camera. There are two types of PoE standards, one is IEEE802.3at, the other is IEEE802.3af. The major difference between them is that PoE+ standard (IEEE802.3at) can pump out up to 30 W per port, whereas PoE standard (IEEE802.3af) can provide up to 15.4 W per port. The question is how to choose or select a best PoE switch for your IP cameras in the perspectives of power supply.
Understand IP Camera Power Needs
The power consumption of PoE IP cameras varies owing to different types e.g. pan-tilt zoom (PTZ) cameras, Dome IP cameras, CCTV cameras, IP cameras with IR illumination night vision, etc. PTZ camera could draw up to 20 Watts, while other IP camera could consumes as little as 3 or 4 Watts. Therefore, a PoE switch should be able to provide enough power for different types of IP camera via Cat 5 or Cat 6 cables.

Although Security cameras, either CCTV cameras or PoE IP security cameras, are not energy-consuming as other gadgets like computers or TVs; they only need a very little electricity to work, you still need to count it in. Remember to double check your PoE IP camera power consumption ether in the user manual or technical specification spreadsheet.
To provide the proper amount of power for PoE IP cameras, another important feature to look for in a PoE switch for IP cameras is its abilities to automatically adjust voltage accordingly. Many security cameras run either 12V or 24V power, if not supplied with the proper power voltage, the IP camera either won’t work or even be overloaded.
Maximal Power Supply of PoE Switch
Besides the power consumption of IP cameras, the maximal power supplies of your PoE switch matters as well.
If the maximal power supply of all your cameras exceeds your PoE switch power cap, then the PoE switch won’t provide enough power for your PoE IP cameras, pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) IP cameras in particular. Insufficient power supply to the IP cameras are the common culprits for video loss and IP camera poor performance.
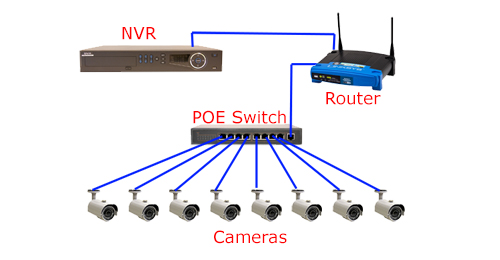
That being said, when buying a PoE switch for IP cameras, it’s important to go for a PoE switch with more power juice or reducing the number of PTZ IP cameras plugged into the PoE switch as PTZ cameras draw more power than other IP cameras.
Can Cat5 Ethernet Cables Cover PoE Transmission Range?
The transmission range of PoE network is 100 meters. PoE IEEE802.3af standard requires powered sourcing equipment (PSE) output power is 15.4W, after 100 meters transmission, the powered devices (PD) can receive 12.95W power. According to 802.3af standard current value-350ma to calculate, the resistance value of 100 meters Ethernet cable should be (15.4-12.95W)/350ma = 7 Ohm or (15.5-12.95)/350ma = 7.29 Ohm.
Obviously, Cat5 Ethernet cable can meet the requirement, but nowadays customers tend to use Ethernet cable Cat5e.
Conclusion
PoE switch is not only the device that provides data connection and electric power to IP cameras, but other PoE devices such as wireless access points, VOIP phones, and NVR recorders. Therefore, when choosing PoE switches, you should count all the devices that you meed to connect with. As a professional telecom supplier, our products including IP cameras, PoE switches and Cat5 cables, are thoroughly tested for use with video surveillance equipment. If you have questions about which PoE power supply is recommended for your security application, please contact us directly.
Original Source: www.fiber-optic-solutions.com
Optical Transceivers for Cisco 300 Series SMB Switch
Cloud is the hot issue, and its fast adoption rate is mostly happening in larger organization. To make every money count in small business network, Cisco and other telecommunication vendors release small and medium-sized business (SMB) switches to stay ahead in a competitive marketplace. Cisco 300 series SMB switch is the fixed-configuration Ethernet switch, which features high-performance, easy-to-setup and energy efficiency. Are you ready to learn more about it? Do you know how to choose fiber optics for Cisco SMB switches?
Networking News for SMB Switch
According to analysis, in the last five years, SMB cloud adoption nationwide has gone through the roof due to the need for scalability and deployment. However, 60% of hacked SMBs go out of business after six months due to the security issue. Furthermore, 70% of the SMB haven’t deployed mobile management solutions for phones and other devices, which makes it even better if you can get ahead of the game. Cisco small business switches, featured with increased revenue, excellent efficiency and strengthened security, provide a better way to do IT. Figure 1 shows 28 Ports 10G SMB Switch.

Cisco 300 SMB Ethernet Switch—Powerful and Affordable
The Cisco 300 Series switches is part of Cisco Small and Medium-sized Business line of network solutions. These switches offer the perfect combination of affordable and advanced networking for small businesses, and help you create a more efficient, better connected workforce. Cisco 300 series are available with 8 to 48 ports of Fast Ethernet and 10 to 52 ports of Gigabit Ethernet connectivity, providing optimal flexibility to create exactly the right network foundation for your business.
Choose the Cisco Small Business Switches for:
- Strong security: a high level of security and give you finegrained control to safeguard your network from unauthorized users.
- Power over Ethernet: with up to 48 PoE ports of Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet connectivity.
- Support: with Cisco Small Business Support Service.
- Advanced management options: with Web-based and command-line interfaces.
- Performance: through VLAN scalability and a non-blocking switch fabric.
- Intelligence: with security and quality of service.
- Fan-less for quiet operation.
Models in Cisco 300 Small Business Switch:
Cisco SF 300-08, SF 302-08, SF 302-08MP, SF 302-08P, SG 300-10, SG 300-10MP, SG 300-10P, SG 300-20, SF 300-24, SF 300-24P, SG 300-28, SG 300-28P, SF 300-48, SF 300-48P, or SG 300-52 Managed Switch. Take Cisco SG 300-10 gigabit switch as an example, it is the fixed configuration managed switch with 2 Gigabit Combo Ports (RJ45+SFP).
You can buy Cisco SG 300-10SFP 8-Port Gigabit SFP Switch with $457.67 in cozlink, or FS S3700-24T4S (24*10/100/1000Base-T Ports+4*10G SFP+) SMB Ethernet Switch at $289.
Unmanaged SMB Switch—Is It the Choice for Small Business Network?
Cisco Small Business Unmanaged Switch is the most cost effective scenarios that require only basic layer 2 switching and connectivity. As such, they fit best when you need a few extra ports on your desk, in a lab, in a conference room, or even at home. With unmanaged switches installed in your network, you can even get capabilities such as cable diagnostics, prioritization of traffic using default QoS settings, Energy savings capabilities using EEE (Energy Efficient Ethernet) and even PoE (Power Over Ethernet).
However, as the name implies, these switches generally cannot be modified/managed. You simply plug them in and they require no configuration at all. Therefore, Many customers prefer to use managed switches.
Cisco Transceiver Module for Compatibility Information
Supported SFP modules are listed below:
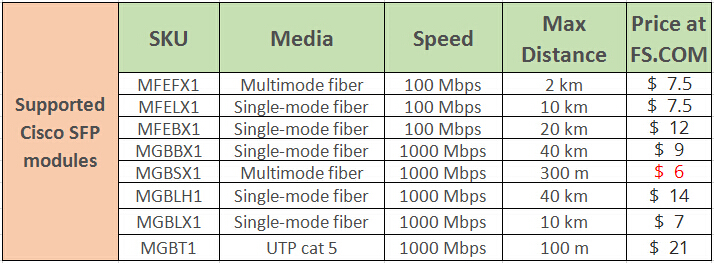
Based on the SFP (optical module form factor) Gigabit Ethernet standards, Besides the above Cisco SFP optics, 1000BASE-T, 1000BASE-SX, 1000Base-LX/LH, 1000BASE-ZX, 1000BASE-BX-D, 1000BASE-BX-U, 1000BASE-EX can be also used with Cisco small business 300 Series SMB switch.
Summary
The Cisco 300 series SMB Switches have been tested to deliver high availability and performance. This solution provides powerful and affordable services, e.g. speed up file transfer times, improve slow, sluggish network, keep business applications available and prevent costly downtime. These Ethernet switches support a huge number of Gigabit Ethernet SFP optical transceivers. You can find all the compatible ones at FS.COM. Besides SMB switches, we also offer 40G/100G data center switches with professional tech support.
Original Source: Cisco 300 SMB Ethernet Switches
400G CFP8 PAM4 & 400GBASE-SR16 NRZ Transceiver Modules
With the price of 100G QSFP28 optics and CFP form factors (CFP module/CFP2/CFP4) dropping down in 2017, 100G technology is becoming more and more popular among data center managers and IT pros in order to cope with the ever-lasting bandwidth needs. However, 100G is not the finish line. CFP multimode source agreement (MSA) demonstrated CFP8 (16X 25 Gb/s) form factor for 400 Gigabit Ethernet at OFC 2017. Although CFP8 module is still in development, it is assured to be popular in the near future. Therefore, this article will have a clearer introduction to 400G CFP8 PAM4 and NRZ modules, and compare with the former CFP modules and 400G CDFP.

Introduction to 400GbE CFP8 Modules
CFP8 module is the latest developing CFP from factor version, which supports eight times and four times the bandwidth density of CFP and CFP2 form factors, respectively. The CFP8 interface supports up to 16 different lanes in each direction with nominal signaling rates of 25Gb/s or 26Gb/s per lane, and either NRZ or PAM4 signaling. As the above image shows, CFP8 is approximately the size of a CFP2 optics. This interface has been generally specified to allow for 16 x 25 Gb/s and 8 x 50 Gb/s mode.
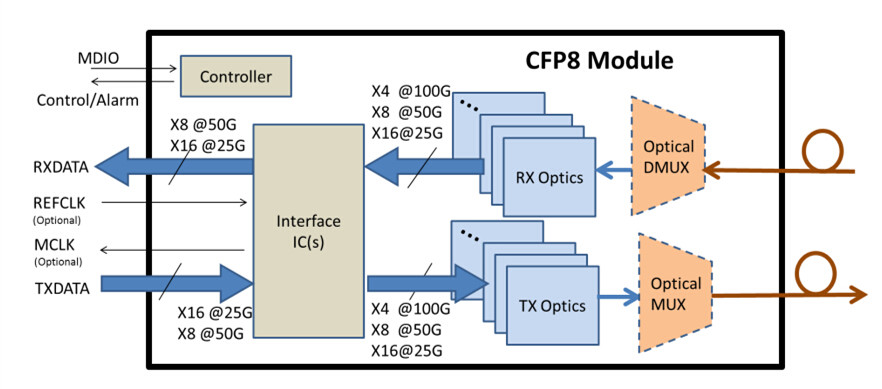
Example IEEE specifications supported by CFP8:
- 400GBASE-SR16 parallel MMF (16x25G NRZ)
- 400GBASE-FR8/LR8 duplex SMF (8x50G PAM4 WDM)
- 400GBASE-DR4 parallel SMF (4x100G PAM4)
- CDAUI-16, CDAUI-8
400G CFP8 FR8 and LR8 Transceivers with PAM4 Technology
CFP8 PAM4 optics, compliant with IEEE 802.3bs 400GBASE-FR8 & LR8 electrical interface specifications, offers higher receiver bandwidth capacity for reach up to 2km and 10km. The 400GBASE-FR8 & LR8 consumes less than half the power per GB compared to a 100G CFP4 msa solution. CFP8 optics uses LC duplex fiber cables.
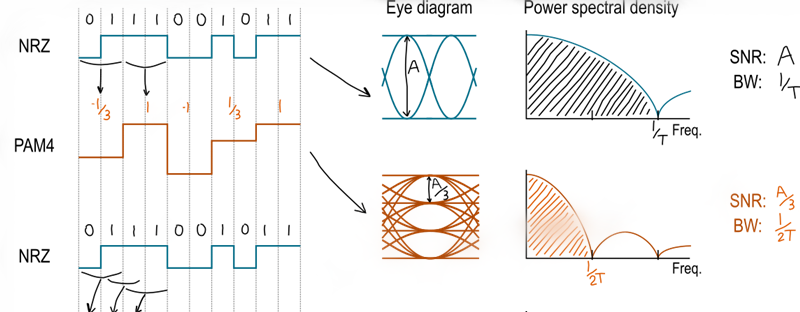
The PAM4 stands for pulse amplitude modulation with four levels. Instead of driving the laser to generate one of the two output amplitudes, like NRZ, PAM4 technology generates four different amplitude levels, meaning a network based on PAM-4 can send twice as much data as an NRZ version.
CFP8 400GBASE-SR16 with NRZ Technology
CFP8 400GBASE-SR16 modules focus on non-return to zero (NRZ) signal modulation Scheme. To use an analogy, it means you’re sending signals in the most simple format: “light on” and “light off.” A ‘1” is transmitted as pulse of light whereas ‘0” is no light output. Based on the currently available fast VCSEL light sources only achieving data rates of 25G, sixteen channels must transmit in parallel to create a 400G data stream.
Due to the design simplicity NRZ, the modulation format of choice for all data rates up to 25Gb/s. 400GBASE-SR16 CFP8 transceivers requires 16 fiber pairs to support a total of 400Gb/s with MPO multimode cables.
What’s New With CFP8 Module?
A CFP8 module is a hot pluggable module. Compared with the former modules, the control and status reporting functions between a host and a CFP8 module use non-data control and status reporting pins on the 124-pin connector. There are three Hardware Control pins, two Hardware Alarm pins, and four pins dedicated to the MDIO interface.
Compared to CFP2/CFP4 MSA Optics
CFP8 is the proposed CFP8 from factor by MSA member companies. It maintains the large size of CFP form factor (nearly the size of CFP2, larger than CFP4 MSA modules), but supports 4x100G i.e. 4x the CFP2. Besides this, CFP8 uses less power than the former CFP form factor modules. There are 400GBASE-SR16 for parallel MMF 16x25G NRZ, and 400GBase-FR8/LR8 duplex SMF 8x50G PAM4 WDM.
CFP8 Vs. CDFP
CFP8 is not the first released 16x25G= 400G modules, but CDFP. 400G CDFP module (CD=400 in Latin), is the four generation CFP form factor. Providing a high level of integration, performance and long-term reliability, the CDFP 400 Gbps interface is available in short- and long-body versions. The specifications are compatible for use with direct attach cables, active optical cables, and connectorized optical modules. The CDFP module will support:
- 5 meter direct attach cables
- 100 meter multimode fiber
- 500 meter parallel single‐mode fiber
- 2 kilometers of duplex single‐mode fiber
The compact modules are well suited for low power applications using copper, VCSEL or silicon photonics based technology. They also targeted InfiniBand EDR hydra cables and 128GFC applications but so far little market segment pick up. Though relatively new with 2014 and 2015 rev releases, CDFP may be short lived due to the smaller more efficient developing set of CFP8 solutions.
Latest Trend With 400 Gb/s in the Industry
While 400 GbE standard is still a few years away, the need for 400 Gb/s interfaces is here today. The CDFP form factor is already being used in proprietary interfaces to interconnect high performance servers and will soon be used to interconnect switch and router chassis. 400G CFP8 FR8/LR8 PAM4 and 400GBASE-SR16 modules had been displayed at OFC 2017. Finisar, Fujitsu, and oclaro, etc MSA member enterprises will introduce low profile 400G modules in a short period.
These proprietary chassis interconnects have always been massively parallel and will continue because they provide the massive bandwidth needed to interconnect equipment so that multiple chassis perform as one big chassis. While 16 lanes is a fairly wide interface, multiple applications need the maximum amount of bandwidth that can only be provided by many parallel lanes running at the fastest speed available. It seem that CFP8 with the same 16 MPO connectors has much potential than CDFP modules. FS.COM offers a large stock MSA-compliant optical transceivers, including 100G CFP/CFP2/CFP4 MSA, CXP, and QSFP28 transceiver modules. We will keep in path with the informative world, and provide the best services & telecom products to all of our customers.
Original Source: 400G CFP8 PAM4 & 400GBASE-SR16 NRZ Transceiver Modules
100G CFP Transceiver – Ultra High Speed Transmission Solution
During the past few years, 40G technology has dominated telecommunications. But now, with the introduction of the 100G technology, everyone is talking about 100 Gbps as the next generation. Whether willing or not, IT managers and data center designers have to consider migrate their network to 100 Gbps in the near future. And CFP is designed to fulfil the deployment of 100G network for companies and enterprises.
Brief Introduction to 100G CFP Optics
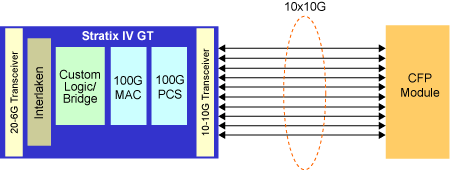
CFP transceiver was designed after SFP transceiver interface, but it supports much larger internet speed, which is realized by using 10×10Gbit/s in each direction (RX, TX). Here the C stands for 100 in Roman numerals (centum). We can infer from the name that CFP is introduced to serve as optical transceiver for 100G interfaces. Since the electrical connection of the CFP uses 10×10Gbit/s lanes in every direction, the optical connection can support both 10×10Gbit/s and 4×25Gbit/s variants of 100Gbit/s interconnects (typically known as 100GBASE-LR10 and 100GBASE-LR4 in 10km SMF reach, and 100GBASE-ER10 and 100GBASE-ER4 in 40km SMF reach, and 100GBASE-SR10 in 100 meter MMF reach respectively.)
Different Types of 100G CFP
There are several CFP types to be introduced—CFP, CFP2 and CFP4. CFP2 and CFP4 are the upgraded generation of CFP. Among them, the size of CFP is the largest. CFP2 is half the size of CFP while CFP4 is the half size of CFP2. And the features of the three different types have been summarized in the following texts. One thing that needs to be noted is that although they are not interchangeable, but could be interoperable at the optical interface with appropriate connectors.

Features and Benefits of CFP:
- Supports 40G and 100G Ethernet CFP optical transceivers
- Capable of side by side mounting as well as “belly to belly” mounting
- Provides full EMI shielding
- Uses a universal rail for both left and right positions
- Allows integration of host PCB to host bezel (face plate) by either of two methods for manufacturing flexibility.
Features and Benefits of CFP2 and CFP4:
- Up to 28 Gbps per lane – 2.8 times faster than current CFP products
- High density, 0.6mm contact pitch
- Provides one of the industry’s leading Signal Integrity (SI) performance for 28 Gbps per lane
- Features a ruggedized cage construction for a more robust solution to help mitigate cage warping
- Flexible design options to address your needs including ganged cages, heat sinks, single-sided and belly-to-belly mounting styles, light-pipes, and the capability to support mid- to long-reach applications
FS 100G CFP Solution
As one of the leading providers in optical communication , FS provides customers with transceivers that are manufactured at the highest quality of standards in the industry. All the CFP transceivers mentioned above, including both CFP2 and CFP4, are available in our website. And every transceiver is individually tested on corresponding equipment such as Cisco, Arista, Juniper, Dell, Brocade and other brands, and passed the monitoring of our intelligent quality control system. Also, all the products in FS are fully warranted against defects in material and workmanship with a lifetime guarantee.
Conclusion
2017 has witnessed the prosperity of the telecommunication market. Many research company predicts that the market of 2018 for telecommunication field will continue to thrive. With such a bright future, fiber optics market attracts a wide attention and many vendors want a piece of the pie. At present, 40G is ubiquitous in the data center and 100G is accelerating. As for the optical transceiver, it has been developed in the past decades to adapt to the high-speed requirement from 1G to 40G even to 100G. Believe it or not, 100G is on the way. Don’t wait to get fully prepared for the upcoming 100G era with CFP transceivers.
Source : 100G CFP Transceiver – Ultra High Speed Transmission Solution
OM5 Fiber Cable – Is It Worthwhile for 40G/100G SWDM4 Cabling Solution
OM5 multimode fiber, as the advanced version of the old OM4 fiber, is thought to be the future of multimode cabling. It is the Wideband multimode fiber (WBMMF) that can support wavelengths between 850nm and 953nm. It is also designed to support the short wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM)—one of the new technology for 40G/100G connection. However, will it be the ideal transmission medium for 40GbE/100GbE cabling solution?
How OM5 Fiber Developed
Over the past thirty years, multimode fiber has been evolved from OM1 to OM5 multimode fiber. OM1 and OM2 fiber, released at the end of 20th century, are the legacy 125µm multimode fiber that are working fine in 10Mb/s, 100Mb/s and 1000Mb/s cabling solution. However, with the high speed data rate like 10Gb/s, 40Gb/s, 100Gb/s and beyond coming into our life, multimode cabling (OM1 and OM2 ) with LEDs can not meet the requirement. The laser-optimized OM3 and OM4 has been developed subsequently. OM4 fiber cable, with the internal construction, possess higher modal bandwidth than OM3 fiber, which is commonly used fiber medium for 40G/100G connection.
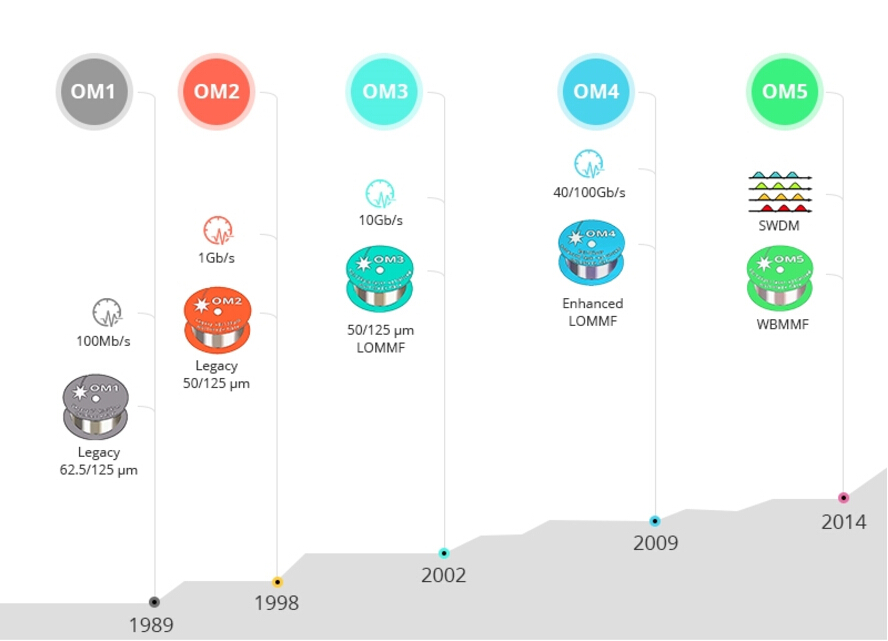
But there is a problem. In a 40G layout, fiber optic technicians have to use one MTP fiber and 4 OM4 duplex fibers (total 8 fibers), which is obvious not preferable for high-density cabling networks. So here comes the OM5 fiber. By utilizing SWDM technology, it can greatly reduce fiber count into 2 fibers (4×10G) in 40G networks, 2 fibers (4×25G) in 100G links. OM5 is the lime green multimode fiber, displayed as follows.
OM5 Fiber for 40G/100G SWDM Cabling Solution
Reduce fiber count for 40G/100G connection—OM5 fiber as the advanced version of OM3/OM4 fiber, is backward compatible with OM3 and OM4 fiber cabling. And with the SWDM technology, this fiber can only use two OM5 fibers and 40/100G SWDM4 transceivers in 40G and 100G SWDM4 cabling.
Longer-transmission distance—OM5 is designed and specified to support at least four WDM channels at a minimum speed of 28Gbps per channel through the 850-953 window. Compared to OM4 fiber cable, it is specified only to work at the 850 nm window. OM5 multimode fiber delivers higher value to network owners for distances up to 440m (for data rates up to 40Gbps), and allows for smooth migration to 400Gbps for distances up to 150m. While OM4 fiber cover the distance of 350m, 100m over 40G/100G respectively.
Easy management & installation—in 40G/100G network, multimode connectivity together with MTP/MPO systems makes for a more user-friendly solution for data centers as well as building and campus backbones, especially in cable installation, troubleshooting, cleaning, and overall maintenance.
FS OM5 Cable Solution
FS offer Lime green OM5 fibers. All our OM5 fiber cables are guaranteed by End Face Geometry Test, Continuity Test, and 3D interferometry Test to be high quality. Available in LC, SC, FC, ST, etc. Connectors, and the cable length of OM5 fiber can be provided from less than 1 meter to more than 100 meters, which will well meet the needs for 400m transmission of 40G SWDM4 QSFP+ module and 100m transmission of 100G SWDM4 QSFP28 module, as well as the links on the same rack or row.
Not only the OM1/OM2/OM3/OM4/OM5 fibers are provided, but singlemode fibers (OS1/OS2) are also offered. For more information about the detailed information of the cost-effective fiber patch cables, Please feel free to contact us via www.fs.com.
Ubiquiti Unifi Switches Vs Cisco Catalyst 2960, Which One Should I Choose?
Recently, the hot debate between Cisco and Ubiquiti Unifi switches has aroused much attention. Data center managers reckon that Cisco catalyst series switch is undoubtedly the ideal choice than UBNT Unifi switches. While small enterprises have to choose the much cheaper Unifi switches. In the ideal world, they’d love to go with Cisco catalyst 2960, but with a limited budget, they can do nothing about it. So basically, this article will help you look for the best options between Cisco Catalyst 2960 and Unifi switches.
Takes a Big Leap With Cisco Catalyst 2960
Cisco Catalyst 2960 series switches are the layer 2/layer 3 edges, providing 10 and 1 Gigabit Ethernet uplink flexibility, Power over Ethernet Plus(PoE+) access connectivity for enterprise, midmarket and brand office networks. There are Catalyst 2960-S and 2960-X series switches.
Cisco 2960-S is the previous layer 2 access switch with the switching capacity of 176Gbps, 2 20G or 4 1G uplinks and PoE/PoE+ up to 740W. Cisco 2960-X/2960-XR switches provides the convenience with layer 2 and layer 3 in a single switch with switching capacity of 216Gbps.
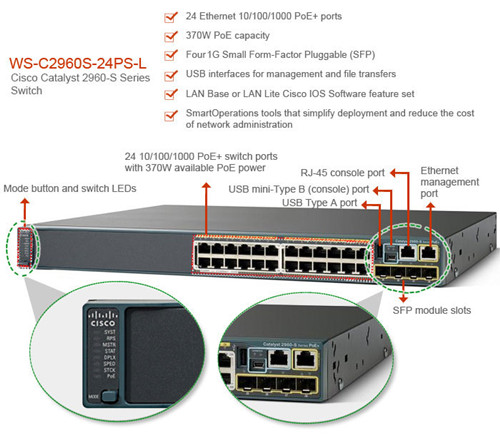
Figure 1 shows Cisco WS-C2960S-24PS-L switches and its features.
FS.COM also offers compatible Cisco 2960 SFP modules, which are 100% tested assured. You don’t need to worry about the our Cisco 2960 x SFP compatibility.
The Benefits of Deploying Catalyst 2960 Switches
- Scale/Performance
Cisco 2960 series supports gigabit access growth for wired and wireless/802.11ac, and more traffic through IP address scalability. And with PoE/PoE+ capacity, Cisco 2960 can be easily and rapidly deployed in many IP endpoints.
- Efficient Switch Operation
Cisco Catalyst 2960 series switches provide optimum power savings, low power operations for industry best-in-class power management, and power consumption capabilities. The Catalyst 2960 ports are capable of reduced power modes so that ports not in use can move into a lower power utilization state. In all, Cisco Catalyst switches reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase energy cost savings and sustainable business behavior.
- Sustainability
Cisco Catalyst 2960 Series Switches include the following features sets: Cisco EnergyWise technology, efficient switch operation, intelligent power management. Cisco Catalyst switching solutions enable greener practices through measurable power efficiency, integrated services, and continuous innovations such as Cisco EnergyWise, an enterprise wide solution that monitors and conserves energy with customized policies.
Get Big Saving on Ubiquiti Unifi Switches
Unifi Switches is fully managed Gigabit switch, delivering robust performance and intelligent switching for your growing networks. The most popular model of this Unifi Switches is US-24, US-48. According to Ubiquiti networks, Unifi switches have the four following features.

Figure 2 shows the Uniquiti Unifi US-24-250W port analyst.
- Multi-Site Management
A single instance of the UniFi Controller running in the cloud can manage multiple UniFi sites within a centralized interface. Each site is logically separated and has its own network monitoring, configuration, maps, statistics, and admin accounts.
- Optical Fiber Backhaul
Two SFP ports support uplinks of up to 1 Gbps. For high-capacity uplinks, each 48-port model includes two SFP+ ports for uplinks of up to 10 Gbps.
- Non-Blocking Throughput
For its total, non‐blocking throughput, the 24‐port model supports up to 26 Gbps, while the 48-port model supports up to 70 Gbps.
- Switching Capacity
The UniFi Switch offers the forwarding capacity to simultaneously process traffic on all ports at line rate without any packet loss.
What Features Does Cisco Switches Have That Are not Addressed by Ubiquiti?
Cisco—Solid brand and construction
- Solid software packages
- Very ala Carte on their service and components.
- Requires Prior knowledge of Cisco Networking. And configuration help from Cisco.
- Most will feed a good sized area but you have to configure for overlap.
- the controller is a small rack mount box and should be in your data center.
- Simple management
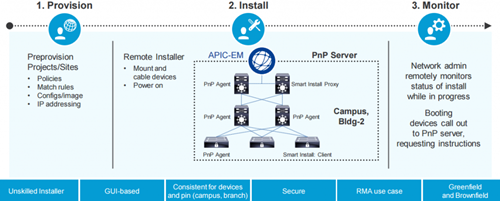
Figure 3 shows the network plug-n-play with Cisco APIC-EM.
What Are the Tempting Points of Unifi Switches, Except Costs?
Ubiquiti—Good Brand and construction
- Good software and easy to understand
- No extra fees other than buying equipment
- If you can program a home router you can set this unit up and the guest network with ease.
- The controller is software based and easy to install and move should the original crap out or need to be reworked.
- You can feed a good size office off of 2 of the Long-Range APs. the controller will handle the overlap for you.
How to Make a Choice Between Ubiquiti and Cisco Switches?
Cost: Price is the biggest incentive in most of the case. A general quote for ubiquiti and Cisco, the Cisco is typically 3 times the cost of ubiquiti. Considering the cost differences between Unifi and Cisco catalyst switches, what makes Cisco so pricey. According to many fiber optic technicians, the ubiquiti system will give them 99% uptime while the Cisco system will give them 99.99% uptime.
Performance: Except the budget, another thing to add into the account is going to be bugs in the code/hardware failures. Within the telecommunication industry, you are not going to find much better, as far as stability is concerned, than Cisco.
Support: With Cisco, you will get some of the best support in the industry. Ubiquiti Unifi switches are quite easy to install and manage. Their controllers are software based, which are quite easy to work with.
Together, If your require a more secure, more robust solution to meet your enterprise and complexity needs, then Cisco is your best option. If you are small to medium sized company and are not trying to create a holo projection of the wheel at every desk. Ubiquiti will be a great fit and should more than meet your needs.
Recommended Information FS.COM 1/10G Enterprise switches supports layer 2 switching capacity featuring Cumulus Linux, Intel Processor, Broadcom Chips, and 176Gbps switching capacity.
Figure 4 shows the S2800 (24*100/1000Base-T+4*GE Combo) switches.
Conclusion
Although there is exact answer to this question, I Insist that you ask several questions inner your mind before taking the next leap. Q1: Is what case would you absolutely need Cisco and Ubiquiti wouldn't do the job? Q2: What features does Cisco products have that are not addressed by Ubiquiti? Q3: Is this the best solution for me? Can I use other branded switches like FS.COM? If you have any comment about this topic, please leave your notes with us.
Four Basic Elements in a WDM System
We know that fiber can carry more data over long distances than any other physical medium. That makes fiber a very precious material. And how to make the most use of your fiber plant becomes a question. So there comes Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM).

Why Should We Deploy WDM ?
WDM can multiply your fiber capacity by creating virtual fibers. The foundation of WDM lies in the ability to send different data types over fiber networks in the form of light. By allowing different light channels, each with a unique wavelength, to be sent simultaneously over an optical fiber network, a single virtual fiber network is created. Instead of using multiple fibers for each and every service, a single fiber can be shared for several services. In this way WDM increases the bandwidth and maximizes the usefulness of fiber. Since fiber rental or purchase accounts for a large share of networking costs, substantial costs can be saved through the application of WDM. Next I will introduce to you the basic four elements in the form of a WDM system.
The Core Technology of WDM System
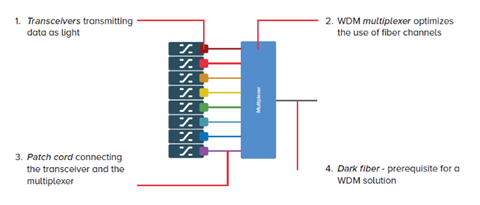
Generally speaking, a WDM system consists of four elements, that are transceiver, multiplexer, patch cord and dark fiber. The following text will explain them to you respectively.
- Fiber Optic Transceivers. Optical transceivers are wavelength-specific lasers that convert data signals from SAN or WAN to optical signals that can be transmitted into the fiber. Each data stream is converted into a signal with a light wavelength that is an unique color. Due to the physical properties of light, channels cannot interfere with each other. Therefore, all WDM wavelengths are independent. Creating virtual fiber channels in this way can reduce the number of fibers required. It also allows new channels to be connected as needed, without disrupting the existing traffic services.
- Optical Multiplexers. The WDM multiplexer, sometimes referred to as the Mux, is the key to optimizing, or maximizing, the use of the fiber. The multiplexer is at the heart of the operation, gathering all the data streams together to be transported simultaneously over a single fiber. At the other end of the fiber the streams are demultiplexed and separated into different channels again.
- Patch cord. The transceiver transmits the high-speed data protocols on narrow band wavelengths while the multiplexer is at the heart of the operation. The patch cable is the glue that joins these two key elements together. LC fiber patch cables are popular, which connect the output of the transceiver to the input on the multiplexer.
- Dark fiber. A requisite for any WDM solution is access to a dark fiber network. The most common way of transporting optical traffic over an architecture is by using a fiber pair. One of the fibers is used for transmitting the data and the other is used for receiving the data. This allows the maximum amount of traffic to be transported. At times only a single fiber is available. Because different light colors travel on different wavelengths, a WDM system can be built regardless. One wavelength is used to send data and a second one to receive it.
Conclusion
WDM has revolutionized the cost of network transport. Thanks to WDM, fiber networks can carry multiple Terabits of data per second over thousands of kilometers with a low cost that is unimaginable less than a decade ago. At FS, we offer a comprehensive portfolio of WDM transmission modules to support the network applications of enterprise and service provider customers. For more details, please visit www.fs.com.
How to Build 10G Network Within Budget
Modern business have become increasingly digital for cloud and data center application, which means everything from sales and marketing to service and support, rely heavily on a fast and reliable network. In 2017, Gigabit Ethernet data rate is no longer adequate to support your business in the ever-developing digital world. Therefore, more and more people nowadays prefers to migrate to 10 Gigabit network. This blog will introduce some basic components of 10G network and how to layout 10GbE within your budget.
How Much Does It Cost?
Three expensive but dispensable elements of 10G network are 10G core switches, access switches with 10G uplinks, and 10G network interface cards for severs and storage devices.
A 10G core switch might cost you $4000 10 years ago, but today, it heavily drops to under $150 per port. Take Cisco 550X and 350X series switches as the example, they offer a full series of 12, 16, 24, 48 10G ports for small and midsize enterprises nearly at $1,500. Obviously, the price can be pretty lower if you search around. For example, Ubiquiti Unifi and Edgeswitch series switches nearly at $200 are suitable for small businesses. FS S3800-48T4S with 48x 100/1000Base-T and 4x 10GE SFP+ is at $480.
For 10G access switches with 10G uplinks, FS S3800-24F4S, S3800-24T4S, S2800-24T4F provides 24 ports with 4 10G uplinks, starting from around $220.
A 10G network interface card (NIC) on severs or storage devices cost usually lower depending on the brand. The hot-selling Mellanox ConnectX series NICs are quite cheap on ebay and Amazon (for under $19).
10G Fiber Optic cabling Elements—10Gbase-T, DAC & SFP+ fiber optics?
When migrating from 1G to 10G, it is simple. Especially with 10GBase-T supported on your 10G switches, you use the same familiar RJ45 network cable to connect the 10G switch with your servers, storage and other switches, and they go up to the same 100 meters as in the Gigabit network. Just make sure you pick up a Cat6a RJ45 network cable instead of the cat5e or cat6a cables. 1m cat6a cables at FS.COM is $3.4. 10GBase-T technology is becoming more popular in network switches and servers because of its lower cost and ease of use. Besides the cat6a/cat7 Ethernet cables, you can also select SFP+ 10GBASE-T modules with 2.5W power consumption and a maximum distance of 30m. SFP+ 10GBASE-T offered at FS.COM is nearly $380.
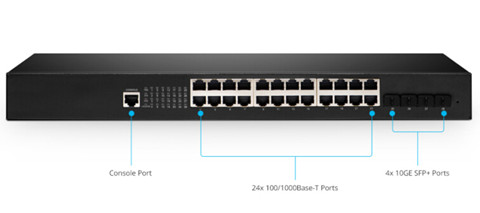
FS S3800-24F4S (seen in the above image), S3800-24T4S and S2800-24T4F also support 10G SFP+. You are recommended to use SFP+ ports if you have existing devices that come with 10G SFP+ port or you need a 10G connection to other switches that are more than 100 meters away.
For servers or storage devices with 10G SFP+ port, the most cost-efficient way to connect is to use SFP 10G DAC (direct attach cable). These are basically copper cables with SFP+ connector on both sides, and they come in limited length of 1m, 3m and 5m. 0.5m copper SFP+ cables at FS.COM is $9.5.

For switches that are more than 100 meters away, you will need a pair of SFP+ modules and the matching fiber cable between them. Depending on the length required, you can use multimode SFP+ and fiber to reach 400 meters and single-mode SFP+ and single-mode fiber optic cables to reach 10 km. For the reliable 10G devices like SFP+ transceivers and fiber optic cables, you can visit FS.COM.
How to Ensure a Smooth 10G Upgrading
You don’t need to rush your whole network to 10GbE in one step. Just start from the core switches that you use to connect all your access switches together and connect your servers and storage devices. Think about how many ports you need and if redundancy is a concern for you. Having two core switches stacked together to provide redundancy and also extra performance is a good design for a solid network foundation.
After upgrading your core switches to 10G, it is time to migrate your key access switches and servers to 10G. You will see immediate performance gain in the most critical parts of your network. The rest of the network can stay as they are for the moment, because 10GBase-T ports are backward compatible with Gigabit links, and 10G SFP+ cage can also work with 1G SFP modules. You can upgrade the rest of your network to 10G whenever you’re ready or in multiple phases if you wish.
Conclusion
I bet you must have a good understanding of what’s between the 10 Gigabit high-performance network. The technology is not complicated, especially with FS 10G switches, Cat6a cables, SFP+ transceivers and SFP+ DAC cables. We will help you build a user-friendly and cost-efficient 10G networks. For more information on FS 10G series switches, please contact us directly.
DWDM System Helps Expand the 10GbE Network
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) network is regarded as the feasible solution to achieve long-distance fiber expansion. DWDM system, with the channel density of 96, has much narrower channel spacing than CWDM system, which allows extremely high utilization of a single fiber strand to pass up to many clients. 10G DWDM SFP+ modules can support a link length of up to 80km. However, the transmission distance of fiber optical network will be affected by factors like date rate, optical signal loss, etc. This article will introduce three instances of how to use DWDM system to extend the transmission distance of 10GbE network.
Basic DWDM Concepts
DWDM uses single-mode fiber to carry multiple light waves of differing frequencies. With the advent of 10G DWDM optics, customers can easily connect up to 80 channels over a single pair of fibers for a maximum distance of 80 km without the need for complicated, bulky and expensive separate DWDM chassis systems. Figure 1 shows the basic working principle of DWDM system.
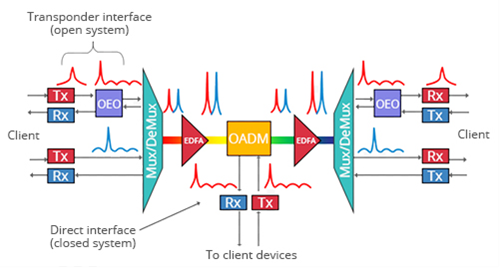
On the client side, the DWDM node converts the local connection to a channelized frequency or wavelength, which is then multiplexed with other lambdas and transmitted over a single fiber connection. The Transponder interface in a DWDM node performs the conversion from the client side grey wavelength to a channelized lambda or colored wave.
The colored wave is then transported to an optical Mux/Demux port matching the tuned wavelength. Mux/Demux multiplexes multiple colored wavelengths together onto an aggregated signal over a single fiber. The aggregated signals are next passed into a Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer (ROADM), which is configured to add specific lambdas from the node to the dark fiber line.
The aggregated signal from the ROADM is then passed on to an amplifier to boost the signal on the outbound connection. The node may also employ a pre-amplifier that boosts an incoming aggregated signal as it comes into the node from another location, prior to passing on to a ROADM to drop or pass signals at that node. This is the ring of DWDM system.
Several 10G DWDM Network Solutions
Different specifications of DWDM have different supporting transmission distances. For example, the theoretical transmission distance of 1G DWDM SFP optical modules can reach 100km, while 10G DWDM SFP+ optical module support theoretically up to 80km, so it is essential to choose a kind of optical module that meets the practical needs. However, in the some cases, we may need to extend the transmission distance of the network without replacing optical module, so that some other devices will be required to ensure the transmission quality of the optical signal. Here we will take the DWDM network of 10G DWDM SFP+ optical module as an example to explain the fact that how to extend transmission distance by increasing devices.

- Instance 1: 31km DWDM network
There are two strands of optical signal transmitted between site 1 and site 2, which are operated over C21 and C50 10G DWDM SFP+ transceiver modules separately. The 80km DWDM SFP+ module can support an actual distance of 31 km without increasing other devices, and the data transmission rate can reach to 10Gbps. The light loss of whole solution is 9dB. 40CH DWDM mux/demux is needed for future proofing.

- Instance 2: 57km DWDM network
For longer distance of the DWDM network, OEO is required to transfer all the regular signals into DWDM signals to decrease the risks of fault caused by high power consumption. According to the figure 3, there are two 1G signals and eight 10G signals that are operated on different wavelengths with 80km DWDM modules between site A and site B. The actual linking distance of this layout is 57km with the light loss of 17dB.
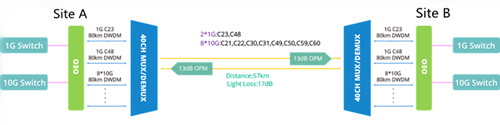
- Instance 3: 24km + 47km DWDM network
This solution is the backup plan for instance 2. To overcome the light loss, apart from deploying OEO and DWDM MUX/DEMUX, OADM is also necessary to support the same 6 wavelengths added in Site 4 to ensure Link D and Link E to work independently.
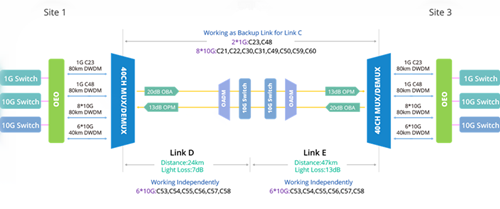
Conclusion
The three instances above are the actual calculated transmission distance of 10G DWDM networks. The solution seems to be quite easy, but you need to pay attention to the optical loss and the budget of dispersion compensation. Besides the DWDM optics, FS.COM offers a full range of WDM devices including EDFA. OEO, DCM, OLP, VOA, etc. For the detailed information about the above layout, please contact us directly.
Introduction to 10GbE/25GbE/40GbE/100GbE Fiber Optic Cabling
Technology is changing rapidly. Just when you got used to Gigabit Ethernet speeds being a fast & reliable system, someone unveiled 10GbE, 25GbE, 40GbE or even 100GbE systems a few years later. The newer and higher performing iterations are indeed the great breakthrough for telecommunication industry, but also pose difficulty in choosing network migration path—10G to 40G to 100G, or to 25G to 50G to 100G. We have described 10G, 25G, 40G and 100G Ethernet technology before, now in this blog, we’d like to introduce the four fiber optic cabling, and compare two 100G migration paths.
10 Gigabit Ethernet technology defined by IEEE 802.3ae-2002 standard, is matured nowadays. Just like the “old” Gigabit Ethernet, 10Gb network can be terminated with either copper or fiber cabling. 1000BASE-T standard usually uses the Cat5e cables as the transmission media, while 10GbE bandwidth requires high grade copper cables like Cat6/Cat6a/Cat7 cables to support 10Gbps data rate. For instance, 10G SFP+ 10GBASE-T transceiver modules utilize Ethernet copper cables (Cat6a/Cat7) for a link length of 30m. SFP+ direct attach cables (DAC) and active optical cables (AOC) are also regarded as the cost-effective solutions for 10G short-reach applications. Besides 10G copper cables, there are single-mode (OS2) and multimode fiber patch cables (OM3/OM4) applied to different 10GbE IEEE standards. For the detailed information about the 10G cabling options, please see the following table.
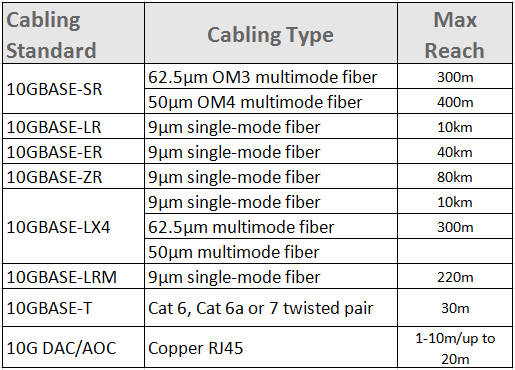
As to the 10G fiber optic transceivers, there are a series of optical form factors including the XENPAK, X2, XFP, SFP+. The former three 10GbE optical transceivers were released earlier than smaller 10G form factor—SFP+ module. However, owing to their larger footprint, they are not successful on the 10G hardware market. Furthermore, SFP+ optics, compliant with several IEEE standards (SR, LR, LRM, ER, ZR and 10GBASE-T...) wins the heart of 10G end-users.
When 25G Ethernet was developed to support a single-lane 25Gbps standard in 2014, it was treated as the “new” 10GbE technology but delivers 2.5 times more data. Compared to 40GbE that was based on 10GbE, 25GbE with one lane obviously improves the port density and cost requirement. 25GbE network can support both copper and fiber optic cables, seen in the below table.Similar to 10GbE networks, 25G Ethernet physical interface specification supports several 25Gbps capable form factors, including CFP/CFP2/CFP4, SFP28 (1x25 Gbps) and QSFP28 (4x25 Gbps), which is also used for 100GbE. SFP28 25GBASE-SR and 25GBASE-LR SFP28 are two popular 25GbE optical transceiver modules available on the market, the former supports up to 100m link length while the latter allows a maximum transmission distance of 10 km.

The available optical switches of the market do not support direct 25GbE connections using an SFP28 direct attach copper (DAC) cable. It is recommended to use a breakout cable that allows four 25GbE ports to connect to a 100GbE QFSFP28 switch port. FS.COM SFP28 DAC cable lengths are limited to four meters (1m, 2m, 3m, 5m) for 25GbE. And if you prefer a longer length, the 25GbE active optic cable (AOC) solutions are good recommendations.
| 25G Optics SFP28 | Type | Media/Reach |
| All 25G SFP28 Ports | 25GBASE-SR | 50µm MMF / 70m |
| 25GBASE-LR | 9µm SMF / 10km | |
| 25GBASE-AOC | Pre-terminated in 3, 5, 7, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30m lengths | |
| OM4 MMF MTP/MPO | 150m | |
| 25G Copper SFP28 | Type | Media/Reach |
| All 25G SFP28 Ports | 25GBASE-CR Twinax / 'Direct Attach' | Pre-terminated in 1m, 2m, 3m, 5m lengths |
Like the 10GbE fiber optic cabling, there are several IEEE standards of 40GbE transceiver in the whole evolution. 40G QSFP+ optical transceivers are the most commonly used optics for 40G network. So how to choose fiber optic cables for 40G optical transceivers? The following table will help you out.
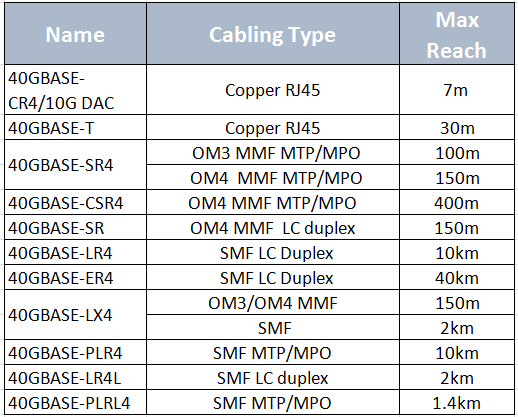
Besides the QSFP+ fiber transceivers and fiber optic cables, 40G DAC cables available in QSFP+ DAC cables and AOC cables enable short-reach options. For 40G cabling, QSFP+ to QSFP+ (40G to 40G) and QSFP+ to 4SFP+ (40G to 10G) breakout cables satisfy customers for various fiber types and reach requirements.
With the price of 100G optics cutting down in 2017, 100GbE network is no longer out of customers’ reach. Telecom giants like Cisco, Arista, HPE launches series of 100G optical switches to meet the market demand. And for other 100G components like 100G optical transceivers, fiber patch cables, racks & enclosures, etc, those are ubiquitous on the market.
100G optical transceivers including the CFP, CFP2, CFP4, CXP and the most popular 100G QSFP28 optics in IEEE standards provide a great selection to the overall users.For 100G inter-rack connections, QSFP28 to QSF28 Direct Attach Copper (DAC) Cables and Active Optical Cables (AOC) as well as the QSFP28 to SFP28 breakout cables are the cost-effective solutions.
This article introduces 10G/40G/100G fiber optic cabling, and make a clear comparison between the two paths to 100GbE. Customers prefer 4×25Gbps for the reasons: Less parallel paths, less fibers, less optics, less everything. For those who want to upgrade from 40G to 100G, appreciate the reliable performance of 40G with the potential to run across 2 parallel 25Ghz rather than 4 required today.
Compatible Gigabit SFP Optical Transceiver for Netonix WISP Switch
The Netonix WISP switch is the managed PoE Gigabit Switches with several Gigabit Ethernet RJ45 and SFP ports. Compared with Ubiquiti Networks Edgeswitch switches (40C), Netonix WISP switches was designed with a rugged chassis and extended operating temperature (-25 to 55C), which is more suitable for outdoor deployment. Furthermore, the ability to power AirFibers is the unique feature of WISP switches. This article will describe WISP switches in detail and help you choose the compatible Gigabit SFP optical transceivers for Netonix WISP switches.
Netonix Gigabit WISP Switches
WISP switches are the Netonix Gigabit switches with the performance of Non-Blocking Throughput Switching and software configuration passive PoE. The Netonix WISP switches feature the ability to power many popular 24V, 48V/50V passive PoE devices from manufacturers including Ubiquiti Networks airMAX™, UniFi™, SAF™, MIMOSA™, Ligowav™, and airFIBER™ product lines. There are WS-24-400A, WS-24-400B, WS-12-250A, WS-12-250B, WS-12-250-DC, WS-12-250-AC, WS-12-DC, WS-10-250-AC, WS-8-250-DC, WS-8-250-AC, WS-8-150-DC, WS-8-150-AC, and WS-6-MINI.

Note that: the No. “6”, “8”, “10”... in those model refers to the numbers of port. And “150” and “250” means the max power consumption. The above image shows the simple home network setup using WS-6-MINI switches.
Optical Transceiver Tested to Work Well in WISP Switches
According to Netonix community, the SFP (optical module form factor) Gigabit Ethernet ports on WISP switches accommodate a full range of SFP optical transceiver modules, including SFP 1000BASE-T, SFP 1000BASE-SX, SFP 1000Base-LX/LH, SFP 1000BASE-ZX, SFP 1000BASE-BX-D, SFP 1000BASE-BX-U, SFP 1000BASE-EX. The following SFP optical transceivers are reported to be working fine on WISP switches.
Major Branded Optical Transceivers For WISP Switches
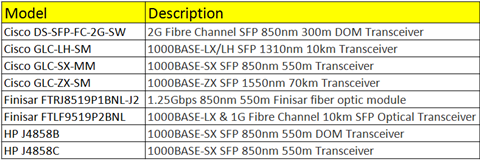
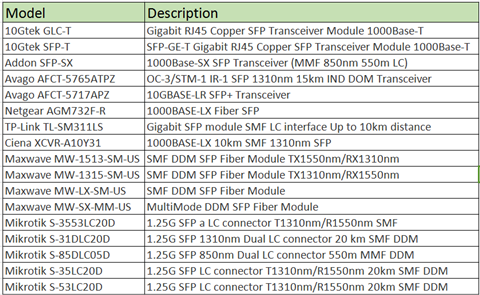
Compatible Optical Transceivers for WISP Switches
Fiberstore compatible optical transceivers are reported to work well on Netonix WISP switches. The following table lists the detailed information about the compatible optical transceiver modules on WISP switches.
Conclusion
The Netonix WISP switches were designed to be part of the Small Business or home networking products that work together as part of proven, fully integrated, easy-to-use small business solution. These switches support a huge number of Gigabit Ethernet SFP optical transceivers. All these high-quality fiber optic transceivers can be found on FS.COM for competitive prices. FS.COM is committed to provide free shipping in USA, Mexico and Australia.
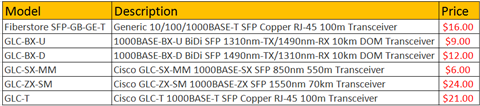
Comparing 10GBASE-T SFP+ Transceiver Module With SFP+ SR/LR Optics & SFP+ DAC Twinax Cables
1000BASE-T SFP modules are available on the market as soon as the certification of Gigabit Ethernet network. However, 10GBASE-T SFP+ modules, owing to the technology limit, have not been supplied by vendors to support 10G copper networks. Instead, IT managers tend to use the cost-effective SFP+ direct attach cables (DAC) for short-reach 10G applications. Today, here comes a big news—vendors like HPE, Prolab, and FS.COM begin to offer 10GBASE-T SFP+ transceiver modules. Do you feel curious about them? This article will unveil the mysterious point of the 10G copper transceivers, and make a detailed comparison with SFP+ fiber modules and DAC twinax cables.
10GBASE-T SFP+ Transceiver Modules
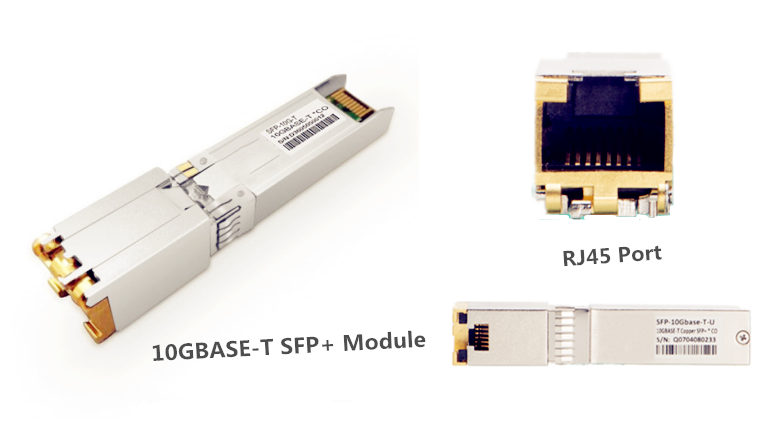
10GBASE-T SFP+ transceiver modules are designed to meet the requirement of 10G longer-reach applications. Compared with SFP+ twinax copper cables (maximum distance is 10m), SFP+ 10GBASE-T transceiver modules operate over Cat6a/Cat7 with a link length of up to 30m. Seen from the below image, SFP+ 10GBASE-T transceiver terminates with a RJ45 connectors, which can be directly used in the RJ45 ports of 10G switches and NIC cards. What’s more, 10GBASE-T SFP+ module is announced to have lower power consumption (2.5W) than SFP+ Twinax DAC cables (4-8W).
Figure 1 shows how to plug a Cat6 cables in a 10GbE SFP+ module.
SFP+ 10GBASE-T Module Vs. SFP+ SR/LR Transceivers
In order to have a better understanding of the 10G copper modules, let’s compare the SFP+ 10GBASE-T modules with SFP+ SR/LR Transceivers and SFP+ DAC Twinax cables.
Both of the SFP+ copper and fiber modules are hot-pluggable with a managed soft-start and are interoperable with any SFP+ cage and connector system. However, they have total different performance when plugging into the 10G switches. SFP+ 10GBASE-T module uses the Cat6a cables for a link length of 30 m over RJ45 connectors. SFP+ SR operates over OM3 cables with a distance of 300m over LC connectors. While SFP+ LR optics utilizes the OS2 LC duplex cables for a distance of 10 km.

Figure 2 shows the SFP+ 10GBASE-T Module (left) and SFP+ SR Transceivers (right).
Note that 10G SFP+ transceivers are nowadays much cheaper than the newly released 10G copper module. For your reference, at FS.COM, Cisco SFP-10G-SR is offered at $16, Cisco stable SFP-10G-LR is &34. While Cisco SFP-10G-T is $380.
SFP+ 10GBASE-T Module Vs. SFP+ DAC Twinax Cabling
Whether to use SFP+ 10GBASE-T module and Cat6a cables or directly use the SFP+ DAC twinax cables for 10G short-reach application, it depends on your own network infrastructure.
- Linking Distance and Power Consumption
As noted before, the maximum linking distance of SFP+ 10GBASE-T module is 30m, while the SFP+ DAC twinax cable is 10m. Furthermore, SFP+ 10GBASE-T module have reduced the power consumption of 10G copper modules, which is a great news for the heavy-loaded 10G data center networks.
- Costs
For 10G intra-rack connection, SFP+ DAC twinax cables obviously cost lower than SFP+ 10GBASE-T copper modules and cat6a cables do. And you should also count the expenditure of 10G switches and NIC cards. 10G switches that can support 10G RJ45 ports are not available nowadays.
- Reliability
Compatible SFP+ Twinax cables have been used for years in 10G networks. So they are quite reliable. As for the SFP+ copper modules, RJ45 interface is rock solid. But many professionals said that technically it could work, but it is not supported for most of the switches. Thus, it is not popular nowadays.
Summary
Customers are very happy to see that there are new products kept coming out to keep in pace with the ever-increasing technology. SFP+ 10GBASE-T copper transceiver is introduced to have a better interoperability between existing fiber switches and 10G copper ports. Although there are still some unsolved problems of SFP+ 10GBASE-T transceiver module, we believe they will be solved in the near future.
How to Choose Fiber Optics for Mellanox ConnectX Ethernet Adapter Cards?
Mellanox ConnectX Ethernet adapter card provides high-performance networking technologies by utilizing IBTA RoCE technology, delivering efficient RDMA services and scaling in ConnectX-3, 4, 5, 6 EN 10/25/40/50/56/100/200GbE connection. The Mellanox ConnectX EN Ethernet card supports a full suite of software drivers like Microsoft Windows (including Windows 10), Linux distributions, VMware and Citrix XenServer. ConnectX Ethernet adapter card comes in several types for 10/25/40/50/56/100/200GbE network, such as ConnectX-3 EN, ConnectX-3 Pro EN, ConnectX-3 Pro EN 10GBASE-T, ConnectX-4, ConnectX-4 Lx EN, ConnectX-5 EN, ConnectX-6 EN adapter cards. In this article, we present an in-depth network-level performance evaluation of the Mellanox ConnectX Ethernet adapter cards and the supported fiber optic cabling.
Network Interface Card (NIC), also known as Network Interface Controller, Network Adapter, LAN Adapter or Physical Network Interface. All Mellanox 10/25/40/50/100/200 Gigabit Ethernet adapters deliver high-bandwidth and industry-leading Ethernet connectivity in enterprise data centers, high-performance computing, and embedded environments. From ConnectX-2 to ConnectX-6, Mellanox keep upgrading their Ethernet adapter cards to meet customers requirement.
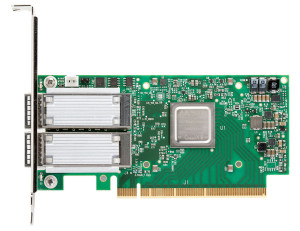
ConnectX-6 EN 200Gb/s Adapter Card, launched last year, was the world-first 200Gb/s Ethernet network adapter card for Ethernet connectivity, sub-600 ns latency and 200 million messages per second. ConnectX-6 EN, seen in the image, provides two ports of 200Gb/s for Ethernet connectivity. As the first adapter to deliver 200Gb/s throughput, ConnectX-6 is the perfect solution to provide machine learning applications with the levels of performance and scalability that they require.
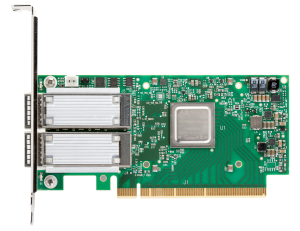
ConnectX-5 just as the image shows, supports two ports of 100Gb/s Ethernet connectivity, sub-700 nanosecond latency, and very high message rate, plus PCIe switch and NVMe over Fabric offloads, providing the highest performance and most flexible solution for the most demanding applications and markets.
Table 1 presents the detailed information about Mellanox ConnectX-5 EN Ethernet Adapter Cards
| Ordering Part No. | Description | Speed | Ports | Connectors | Dimensions w/o Bracket |
| MCX515A-CCAT | 100GbE single-port QSFP28, PCIe3.0 x16, tall bracket, ROHS R6 | 100GbE | 1 | QSFP28 | 14.2cm x 6.9cm (Low Profile) |
| MCX516A-CCAT | 100GbE dual-port QSFP28, PCIe3.0 x16, tall bracket, ROHS R6 | 100GbE | 2 | QSFP28 | 14.2cm x 6.9cm (Low Profile) |
| MCX516A-CDAT | 100GbE dual-port QSFP28, PCIe4.0 x16, tall bracket, ROHS R6 | 100GbE | 2 | QSFP28 | 14.2cm x 6.9cm (Low Profile) |
 ConnectX-4 adapter cards have three different types: ConnectX-4 Lx EN Programmable Adapter Card, ConnectX-4 EN, ConnectX-4 Lx EN. ConnectX-4 Lx EN Programmable Adapter Card is listed in the right image. ConnectX-4 EN network is the single or dual port 100 Gigabit Ethernet adapter cards. ConnectX-4 Lx enables data centers to migrate from 10G to 25G and from 40G to 50G speeds at similar power consumption, cost, and infrastructure needs. If you are into this NIC card, you'd better look through their difference.
ConnectX-4 adapter cards have three different types: ConnectX-4 Lx EN Programmable Adapter Card, ConnectX-4 EN, ConnectX-4 Lx EN. ConnectX-4 Lx EN Programmable Adapter Card is listed in the right image. ConnectX-4 EN network is the single or dual port 100 Gigabit Ethernet adapter cards. ConnectX-4 Lx enables data centers to migrate from 10G to 25G and from 40G to 50G speeds at similar power consumption, cost, and infrastructure needs. If you are into this NIC card, you'd better look through their difference.
ConnectX-3 Gigabit Ethernet interface card is one of the mostly used NIC cards nowadays. This kind of NIC card can support 10/40/56Gb/s Ethernet connectivit y with hardware offload engines. The long-term goal at Mellanox ConnectX Gigabit Ethernet adapter card is to allow customers to wire once and switch protocols on the server and switch as required by workloads. Mellanox can presumably charge a premium for such capability, and ConnectX-3 silicon allows Mellanox to create fixed adapters and switches at specific speeds to target specific customer needs and lower price points, too. The image on the right display the ConnectX-3 Pro Programmable Adapter Cards.
y with hardware offload engines. The long-term goal at Mellanox ConnectX Gigabit Ethernet adapter card is to allow customers to wire once and switch protocols on the server and switch as required by workloads. Mellanox can presumably charge a premium for such capability, and ConnectX-3 silicon allows Mellanox to create fixed adapters and switches at specific speeds to target specific customer needs and lower price points, too. The image on the right display the ConnectX-3 Pro Programmable Adapter Cards.
For detailed information about ConnectX-3 Pro EN adapter cards, please see the Table 2.
| Ordering Part No. | Description | Dimensions w/o Bracket |
| ConnectX-3 Pro EN Adapter Cards | ||
| MCX311A-XCAT | Single 10GbE SFP+ | 10.2cm x 5.4cm |
| MCX312A-XCBT | Dual 10GbE SFP+ | 14.2cm x 6.9cm |
| MCX313A-BCBT | Single 40/56GbE QSFP | 14.2cm x 5.2cm |
| MCX314A-BCBT | Dual 40/56GbE QSFP | 14.2cm x 6.9cm |

Mellanox ConnectX-2 EN cards are the older cards for Ethernet only. That means that they will not work in Infiniband networks. In fact, there are still a few examples of OSes without ConnectX-2 support. Prime examples are FreeBSD 9.3 based FreeNAS and NAS4Free versions which did not have built-in support for the cards. The bottom line is that in terms of compatibility, one does need to verify these cards will work.
Many customers do use these in their Windows 10 home workstation for a 10Gb SFP+ back-haul network. Speeds are reliable and excellent. Nowadays, Mellanox does not supply this card, but ebay and Amazon do provide ConnectX-2 cards under $19.
According to Mellanox, ConnectX-3 10G/40G/56G Ethernet adapter cards are interoperable with 10/40 Gb Ethernet switches. Passive copper cables with ESD protection are supported in this NIC card. ConnectX-3 cards can support up to 56Gb/s that can accommodate several fiber cables and optical transceiver types. Take the MCX313A-BCBT as an example, it has single 40GbE QSFP+ port. QSFP+ optical transceivers and DAC cables are feasible in this Ethernet Adapter Card. For the 10G SFP+ to 40G QSFP+ migration, Mellanox QSA (QSFP+ to SFP+) modules are required.

A previous article QSFP+ to SFP+ Adapter (QSA) Module Vs. QSFP+ to SFP+ Breakout Cable provides the detailed information about how to use the QSA module.
Mellanox ConnectX EN Gigabit Ethernet Cards can support up to 200Gbps data rate. Each ConnectX adapter card, as mentioned above, supports optical transceivers and modules applied for 10G/25G/40G/100G Ethernet network. ConnectX-2 EN Ethernet card, for example, can be used for 10GbE networks. Except the expensive SFP+ optical transceivers, SFP+ DAC Twinax and 10GBASE-T copper cables are the commonly used transmission media for 10G data center inter-rack and TOR switching. So how to choose between them?
DAC SFP+ Twinax cables integrates SFP+ modules and Twinax cables on the same conduit. It uses the SFP+ optical transceiver modules as connectors (not the real transceiver) on both ends so as to provide a cost-effective and low-power consumption solution for data center interconnection. 10G DAC Twinax cables can be divided into two types: active DAC twinax and passive DAC cables. For distances >5m and <10m, pickup the active version. Otherwise passive direct attach copper cables should be fine.

Fiberstore is one of the best vendors for DAC and other fiber optics. Their packaging and after-sale support for even the smallest orders is excellent. For connecting two ConnectX-2 cards together, you can get one of the SFP+ copper cables.
Ethernet Network Cables like Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6 do look alike from the outside and they all use the same connectors as well. However, they have significant differences on the inside. One simple method is that you can find out the type of cable you have by looking at the text printed on the side of the cable. There are other cables possible (like Cat7 and Cat8 cables) but Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6 cables are the most common now.
- CAT5
Category 5 cabling is an older type of network cabling compared with Cat5e and Cat6 cables. Cat5 cables support transfer speeds of 10/100 Mbit/s (Fast Ethernet). Nowadays, many installers treat it as old and obsolete and try not to use it. For those who buy cat5 cables, they tend to use in older devices such as an older router or switch.
Category 5 enhanced (Cat5e) cables currently are the most commonly used Ethernet network cables owing to its enhanced transmission data rate and reduced crosstalk. Cat5e cabling supports 1000 Mbit/s and cust down on external and internal crosstalk. It basically means that Cat5e is better at keeping signals on different circuits or channels from interfering with each other.
- CAT6
Category 6 cabling (Cat6) supports 10 Gbit/s speeds with additional crosstalk improvements. If you're purchasing a new cable for future proofing, it should really be CAT6 or above. That doesn't imply Cat6 cables protect your network from the future or anything, it just means it will keep it up to date for longer when the next products comes along.
Note : Your network speed depends on the slowest part of your setup. If you want to deploy gigabit ports, gigabit routers, switches, then please make sure you cabling also supports those speeds as well.
Mellanox is the world-class vendor for selling multi-protocol chips and adapter cards for servers. It provides a wide range of high-speed interconnection solutions including Gigabit Ethernet cards and InfiniBand adapter cards. The above mentioned ConnectX Gigabit Ethernet cards can not be used in InfiniBand networks. ConnectX Mellanox Gigabit Ethernet cards are the cost-effective devices for your network applications. If you do have the Mellanox NIC cards, you can buy the cost-effective DAC and optical transceiver modules from FS.COM to further reduce the total cost of your budget.
How to Choose SFP Transceiver Modules for UniFi US-8-150W Switch?
Ubiquiti Networks Unifi switch is part of the UniFi line of products that delivers robust performance and intelligent switching for the growing networks. Many customers nowadays hold great feedback about the cost-effective UniFi switches. US-8-150W, as one of the most popular UniFi switches, offers eight Gigabit RJ45 ports and 2 SFP ports that can support up to 1Gbps. So, how to choose the suitable optics for UniFi US-8-150W switch? This article will provide detailed information about this UniFi switch and the appropriate SFP modules for US-8-150W switch (seen in the below image).

Understanding UniFi US-8-150W Switches
Ubiquiti Networks UniFi switches can be divided into two types: managed Gigabit switches and managed PoE+ Gigabit Switches. In short, POE switches and non-POE switches. Each UniFi switch type is fully managed Gigabit switches with RJ45 and SFP+/SFP ports, offering non-blocking throughout switching performance.
US-8-150W UniFi switch features 8 RJ45 ports and 2 SFP ports which offer convenient different power output options, auto-sensing IEEE 802.3af/at POE/POE + performance. It is a bit larger than a standard home switch. So, would-be buyers who are looking to rack mount need to buy a extra shelf and stick it there. The table below provides the clearer information about this switch.
Note that US-8-150W is only US $199.
How to Select SFP Modules for UniFi US-8-150W Switches?
According to Ubiquiti Networks, both their original and third party SFP transceiver modules from other vendors can be used on UniFi switches.
Ubiquiti Networks UF-MM-1G & UF-SM-1G-S
Ubiquiti Networks only offer two type of SFPs—UF-MM-1G and UF-SM-1G-S. UF-MM-1G SFP module supports a data rate of 1.25 Gbps over multimode fibers. It uses the 850nm as the Tx and Rx wavelength with a supporting distance of 550m.
UF-SM-1G-S is a single-mode SFP available in both blue (1310nm) and yellow (1550nm) color code. Unlike the 1000BASE-LX SFP optics with LC single-mode fibers that can operate up to 5 km, UF-SM-1G-S only supports a link limit of 3 km.

Figure 3 presents all the existing fiber optic transceivers (SFP and SFP+) from Ubiquiti Networks. UF-SM-1G-S is in the middle of the image.
3rd Party SFPs for US-8-150W Switch
Besides the above two SFP types, there are several more Gigabit Ethernet standards for SFP transceiver modules—1000BASE-T, 1000BASE-SX, 1000Base-LX/LH, 1000BASE-ZX, 1000BASE-BX-D, 1000BASE-BX-U and 1000BASE-EX, which are compatible with the UniFi switches. According to the Ubiquiti Networks, Fiberstore (FS.COM) SFPs are tested to be fully compliant with UniFi switches. For more information about these compatible SFPs, please check on the following list.
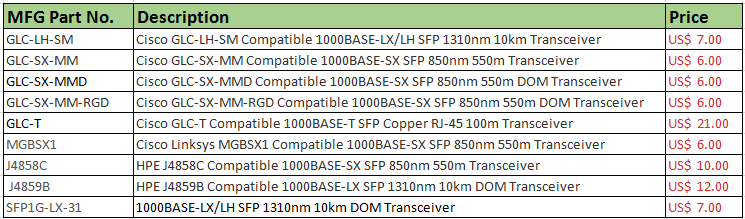
From the table, we know that several Cisco SFP modules and HPE SFP transceivers are working on the UniFi Switches. In our test center, we have tested the GLC-T compatibility and Cisco GLC-SX-MM compatible issues.
More Information About UniFi Switches
Besides the hot selling US-8-150W switches, there are a series of UniFi switches such as US-8-60W, US-16-XG, US-48, US-8, US-24, US-48-750W, US-48-500W, US-24-250W, US-24-500W. Whether you use which one, FS.COM SFPs in the above table are tested to be fully compatible with UniFi switches. For such a low price of the 3rd party SFP transceiver modules, it is advisable for you to purchase more optics for backup.
Summary
The UniFi US-8-150W switches are designed to be part of the complete line of small business or home networking and wireless communication products that work together as part of proven, fully integrated, easy-to-use small business solution. UniFi switches support several types of Gigabit Ethernet SFP optical transceivers. All these high-quality fiber optic transceivers can be found on FS.COM for great prices. We also make sure to provide its customers same day shipping. Some of the items can be directly shipped from Seattle warehouse.
QSFP28 Transceiver With MTP or LC Duplex Cables
Nowadays, QSFP28 transceiver is the mainstream of 100G optics market. So as to meet different 100G deployment needs, QSFP28 modules usually come in several standards such as QSFP28 PSM4, QSFP28 CWDM4, IR4, SR4 and LR4, etc . Compared with CXP and CFP 100G optical transceivers, QSFP28 optics are the smallest form factors that provide a high-density and high-speed solution for 100G networks. A previous article provide detailed information about what distance QSFP28 optics can support for 100GbE deployment. Today’s article will introduce 100G QSFP28 cabling solutions by the use of MTP/MPO cables and duplex LC cables.
QSFP28 modules offer four channels of high-speed differential signals with each data rates up to 28Gbps, and will meet 100 Gbps (4x25 Gbps) in the end. QSFP28 transceiver is available in 100GBASE-SR4, 100GBASE-LR4, PSM4 and CWDM4 standards. The interface of 100G QSFP28 transceivers includes MTP/MPO and LC duplex cables.
Cabling Solutions of QSFP28 MPO
100G QSFP28 100GBASE-SR4 and 100GBASE-PSM4 transceiver modules are the 100G transceiver modules that need to be connected with MTP/MPO interfaces. 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28 complies with QSFP28 MSA and IEEE 802.3bm specifications. It can support a link length of 100 m. 100G PSM4 specification defines requirements for a point-to-point 100 Gbps link over eight single-mode fibers with a supporting distance of 500 m. Figure 1 shows the QSFP28 SR4 with MTP connector.

MTP/MPO fiber cable is commonly used to connect QSFP+ or QSFP28 transceivers with single-mode and multimode categories, which is specially designed for 40G/100G high-density data center cabling system. MTP/MPO fiber cables are usually terminated with 12-fiber, 24-fiber, 48-fiber MTP/MPO connectors. Single-mode MTP/MPO cable is able to carry signal over long distance while multimode is for short-reach application. QSFP28 mpo
- 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28 over Multimode MTP cable
100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28 works over a 12-fiber multimode MTP/MPO patch cable (four not used) for short-reach 100G connection. Figure 2 shows the direct connection between 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28 modules by the use of Female to Female 12-Fibers OM4 trunk Cable.

- 100GBASE-PSM4 QSFP28 Over Single-mode MTP Cable
Similar to 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28, 100GBASE-PSM4 QSFP28 also requires 12-fiber MTP/MPO patch cable. But QSFP28 PSM4 matches with single-mode MTP/MPO fiber patch cable instead of the multimode MTP/MPO .patch cables.
100G QSFP28 Optics With Single-mode Duplex LC Interface
100GBASE-CWDM4 QSFP28 and 100GBASE-LR4 QSFP28 are the 100G modules designed for long-reach applications terminated with duplex LC interface. 100GBASE-CWDM4 QSFP28, as the name implies, it is a full duplex module with the use of CWDM technologies. It integrates transmit and receive path in one module. 4 lanes of optical signals (25 Gbps per lane) firstly are multiplexed into an LC duplex interfaces on the transmitting side. Then data streams are de-multiplexed by an integrated optical de-multiplexer and transformed to an electrical CAUI-4 output driver. QSFP28 CWDM4 can support a distance of 2 km over single-mode fibers. Figure 3 shows the interconnection of 100G QSFP28 LR4 module connected with MTP to LC breakout and MTP cassette to achieve a total 400G data rate transmission.

100GBASE-LR4 QSFP28 is a 4x25Gbps transceiver module that can support link lengths up to 10 km. 100GBASE-LR4 QSFP28 also operates over single-mode fiber cable with duplex LC connector by multiplexing and de-multiplexing optical signals. Common single-mode duplex LC patch cable can meet the cabling requirement of these two transceivers. For high density data center, HD LC fiber patch cable is highly recommended as the push-pull tab is easy to remove and can save space.
Conclusion
With compact size and low power consumption, 100G QSFP28 modules are becoming the most popular 100G optics on the market. QSFP28 SR4 and QSFP28 PSM4 transceivers terminate with MTP/MPO interfaces, while QSFP28 LR4 and CWDM4 modules connect with LC duplex cables. Besides QSFP28 transceivers, there are QSFP28 DAC and AOC cable available for short-reach 100G connections.